Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Prove geometrically that when plane mirror turns through a certain angle, the reflected ray turns through twice the angle.
उत्तर
Consider a ray of light AB, incident on a plane mirror in position MM’, such that BC is the reflected ray and BN is normal.
∠ABM = ∠CBN = ∠i
∠ABC = 2 ∠i …(i)
Let the mirror be rotated through an angle ‘0’ about point B, such that M1M1 is the new position of the mirror and BN1 is the new position of normal. As the position of the incident ray remains same, therefore new angle of the incidence is ∠ABN1 whose magnitude is (i + θ). Let BD be the reflected ray, such that ∠DNB1 is the new angle of reflection.
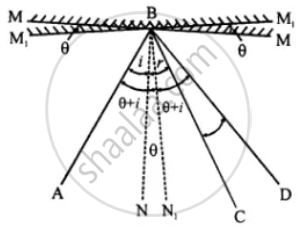
∠ABD = ∠ABN1 + ∠DBN1
= ∠(i + θ) + ∠(i + θ)
= 2 ∠i + 2∠θ
Subtracting (i) from (ii)
∠ABD - ∠ABC = 2∠i + 2∠θ - 2∠i
∴ ∠CBD = 2∠θ
Thus, for a given incident ray, if the plane mirror is rotated through a certain angle, then the reflected ray rotates through twice the angle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a diagram to show the reflection of a light ray incident normally on a plane mirror.
Why is it difficult to read the image of the text of a page formed due to reflection by a plane mirror?
The image formed by a plane mirror is :
An insect is sitting in front of a plane mirror at a distance 1 m from it.
(a) Where is the image of the insect formed?
Prove experimentally that images are formed as far behind in a plane mirror as the object is in front of it.
State the mirror formula for the formation of total number of images formed in two plane mirrors, held at an angle.
Draw a neat two ray diagram for the formation of images in two plane mirrors, when mirrors are at facing each other.
A boy stands 4 m away from the plane mirror. If the boy moves `1/2` m towards the mirror, what is now the distance between the boy and his image? Give a reason for your answer.
Select the correct option:
In case of concave mirror, the minimum distance between an object and its real image is:
