Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A free bird leaps on the back
Of the wind and floats downstream
Till the current ends and dips his wing
In the orange suns rays
And dares to claim the sky.
Read the above lines and answer the question that follow.
Explain with reference to the context.
उत्तर
These lines are taken from the poem, ‘I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings’ written by Mary Angelou. The theme of the poem is the suffering of African- Americans and the contrast of slavery versus freedom. Maya Angelou’s 1983 poem “Caged Bird” compares the plight of a caged bird to the flight of a free bird. Many readers have interpreted Angelou’s poem as an extended metaphor with the caged bird representing the historical struggles of African Americans.
In these lines the poet refers to nature. She describes the way “a free bird leaps on the back of the wind”. She describes the bird’s flight against the orange sky. The free bird has the right “to claim the sky”. The way she describes the “orange sun rays” gives the reader an appreciation for the natural beauty of the sky, and her description of the way the bird “dips his wing” helps the reader to appreciate the bird in his natural habitat, enjoying his freedom.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Thinking about Poem
The poet says “No” in the beginning of the third stanza. What does he mean by this?
Sometimes we see something beautiful and striking, and we remember it for a
long time afterwards. Can you recollect this ever happening to you? If so, what
was it? What do you remember about it now? Are the details of what you saw or
the feelings you experienced at that time fresh in your mind? Think for a few
minutes, then share your thoughts with the class.
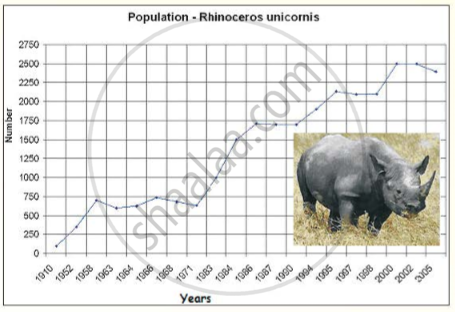
Read this article about the great Indian Rhinoceros. [You will find the information useful for your group discussion in 5.]
The Indian Rhinoceros or the Great One-Horned Rhinoceros or the Asian Onehorned Rhinoceros (Rhinoceros unicomis) is a large mammal primarily found in north-eastern India, Nepal and parts of Bhutan. It is confined to the tall grasslands and forests in the foothills of the Himalayas.
The Indian Rhinoceros once ranged throughout the entire stretch of the Indo Gangetic Plain but excessive hunting reduced their natural habitat drastically.
Today, about 3,000 Indian Rhinos live in the wild, 1,800 of which are found in Assam alone. In 2008, more than 400 Indian Rhinos were sighted in Nepal's Chitwan National Park.
In size it is equal to that of the White Rhino in Africa; together they are the largest of all rhino species. The Great One-Horned Rhinoceros has a single horn; this is present in both males and females, but not on newborn young. In most adults, the horn reachee a length of about 25 centimetres, but has been recorded up to 57 .2 centimetres in length. The nasal hom curves backwards from the nose. The horn is naturally black.
This prehistoric-looking rhinoceros bas thick, silver-brown skin which becomes pinkish near the large skin folds that cover its body. The male develops thick neckfolds. It has very little body hair aside from eyelashes, ear-fringes and tail-brush.
These rhinos live in tall grasslands and riverine forests, but due to the loss of habitat, they have been forced towards cultivated land. They are mostly solitary creatures, with the exception of mothers and calves and breeding pairs, although they sometimes, congregate at bathing areas.
The Indian Rhinoceros makes a wide variety of vocalizations. At least ten distinct vocalizations have been identified: snorting, honking, bleating, roaring, squeak panting, moo-grunting, shrieking, groaning, rumbling and humphing. In addition to noises, the rhino also uses olfactory communication.
In aggregation, Indian Rhinos are often friendly. They will often greet each other by waving or bobbing their heads, mounting flanks, nuzzling noses, or licking. Rhinos will playfully spar, run around, and play with twigs in their mouth. Adult males are the primary instigators of fights. Fights between dominant males are the most common cause of rhino mortality. Indian rhinos have few natural enemies, except for tigers. Tigers sometimes kill unguarded calves, but adult rhinos are less vulnerable due to their size. Humans are the only other animal threat, hunting the rhinoceros primarily for sport or for the use of its horn. Indian Rhinos have been somewhat tamed and trained in circuses, but they remain dangerous and unpredictable animals.
In the nineteenth and early twentieth century, the Indian Rhinoceros was hunted relentlessly. Reports from the middle of the nineteenth century claim that some military officers in Assam individually shot more than 200 rhinos. In the early 1900s, officials became concerned at the rhinos' plummeting numbers. By 1908 in Kaziranga, one of the Rhinos' main ranges, the population had fallen to around 12 individuals. In 1910, all rhino hunting in India became prohibited.
The rhino has been a major success in conservation. Only 100 remained in the early 1900s; a century later, their population has increased to about 2500 again, but even so, the species is still endangered. The Indian rhino is illegally poached for its horn. Some cultures in East Asia believe that the hair has healing and potency powers and therefore is used for traditional Chinese medicine and other Oriental medicines.
The Indian and Nepalese Governments have taken major steps towards Indian Rhinoceros conservation with the help of the World Wildlife Fund (WWF). The Kaziranga National Park and Manas National Park in Assam, Pobitora Reserve Forest in Assam {having the highest Indian rhino density in the world), Orang National Park of Assam, Laokhowa Reserve Forest of Assam (having a very small population) and Royal Chitwan National Park in Nepal are homes to this endangered animal.
Old Kaspar took it from the boy,
Who stood expectant by;
And then the old man shook his head,
And,with a natural sigh,
"Tis some poor fellow's skull," said he,
"Who fell in the great victory.
"I find them in the garden,
For there's many here about;
And often when I go to plough,
The ploughshare turns them out!
For many thousand men,"said he,
"Were slain in that great victory."
Read the lines given above and answer the question that follow.
Why does the poet use a skull?
"They say it was a shocking sight
After the field was won;
For many thousand bodies here
Lay rotting in the sun;
But things like that, you know, must be
After a famous victory.
"Great praise the Duke of Marlbro'won,
And our good Prince Eugene."
"Why,'twas a very wicked thing!"
Said little Wilhelmine.
"Nay...nay...my little girl,"quoth he,
"It was a famous victory.
"And everybody praised the Duke
Who this great fight did win."
"But what good came of it at last?"
Quoth little Peterkin.
"Why that I cannot tell,"said he,
"But 'twas a famous victory."
Read the lines given above and answer the question that follow.
How do the skulls symbolize the theme in “The Battle of Blenheim”?
From the day, perhaps a hundred years ago when he sun had hatched him in a sandbank, and he had broken his shell, and got his head out and looked around, ready to snap at anything, before he was even fully hatched-from that day, when he had at once made for the water, ready to fend for himself immediately, he had lived by his brainless craft and ferocity. Escaping the birds of prey and the great carnivorous fishes that eat baby crocodiles, he has prospered, catching all the food he needed, and storing it till putrid in holes in the bank. Tepid water to live in and plenty of rotted food grew him to his great length. Now nothing could pierce the inch-?thick armoured hide. Not even rifle bullets,
which would bounce off. Only the eyes and the soft underarms offered a place. He lived well in the river, sunning himself sometimes with other crocodiles-muggers, as well as the long-? snouted fish-?eating gharials-on warm rocks and sandbanks where the sun dried the clay on them quite white, and where they could plop off into the water in a moment if alarmed. The big crocodile fed mostly on fish, but also on deer and monkeys come to drink, perhaps a duck or two.
Read the extract given below and answer the question that follow.
What protected him now? How?
What test had Portia’s father devised for her suitors? What oath did the suitors have to take before making their choice?
What do you know about the queen ant?
Who is giving these instructions?
In the poem, The Darkling Thrush, the poet uses the words “evensong" and “carolling” to describe the thrush's song because ______.
