Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Read the passage and answer the questions based on it.
If heat is exchanged between a hot and cold object, the temperature of the cold object goes on increasing due to gain of energy and the temperature of the hot object goes on decreasing due to loss of energy. The change in temperature continues till the temperatures of both objects attain the same value. In this process, the cold object gains heat energy and the hot object loses heat energy. If the system of both the objects is isolated from the environment by keeping it inside a heat-resistant box then no energy can flow from inside the box or come into the box. In this situation, we get the following principle.
Heat energy lost by the hot object = Heat energy gained by the cold object. This is called the ‘Principle of heat exchange’.
- Where does heat transfer take place?
- In such a situation which principle of heat do you perceive?
- How can this principle be explained in short?
- Which property of the substance is measured using this principle?
उत्तर
- Heat is transferred from hot object to cold object.
- During the transfer of heat from hot object to cold object we perceive the principle of heat exchange.
- As inside the heat resistant box, the heat lost by hot object exactly equals heat gained by cold object, principle of heat exchange is stated as:
In an isolated system,
Heat energy lost by hot object = Heat energy gained by cold object. - Specific heat of the substance is measured using the principle of heat exchange.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A child running a temperature of 101°F is given an antipyrin (i.e. a medicine that lowers fever) which causes an increase in the rate of evaporation of sweat from his body. If the fever is brought down to 98 °F in 20 min, what is the average rate of extra evaporation caused, by the drug? Assume the evaporation mechanism to be the only way by which heat is lost. The mass of the child is 30 kg. The specific heat of human body is approximately the same as that of water, and latent heat of evaporation of water at that temperature is about 580 cal g–1.
What amount of heat must be supplied to 2.0 x 10-2 kg of nitrogen (at room temperature) to raise its temperature by 45 °C at constant pressure? (Molecular mass of N2 = 28; R = 8.3 J mol-1 K-1.)
Water in lakes and ponds do not freeze at once in cold countries. Give a reason is support of your answer.
What do you mean by the following statement?
The specific heat capacity of copper is 0. 4 Jg-1 K-1?
The S.I. unit of specific heat capacity is ______.
45 g of water at 50°C in a beaker is cooled when 50 g of copper at 18° C is added to it. The contents are stirred till a final constant temperature is reached. Calculate this final temperature. The specific heat capacity of copper is 0.39 J g-1K-1 and that of water is 4.2 J g-1K-1. State the assumption used.
It is generally cold after a hail-storm then during and before the hail storm. Give reason.
Name two green house gases ?
What impact will climate changes have on the crops of food?
Fill in the following blank using suitable word:
SI unit of heat is .........
What is heat? What is the S. I. unit of heat?
State the condition for the flow of heat energy from one body to another.
If substances A and B are liquids then which one would be more useful in car radiators?
Given: Specific heat capacity’A’ 3.8 J/g /K. Specific heat capacity ‘B’ 0.4 J/g /K.
50 g of copper is heated to increase its temperature by 10° C. If the same quantity of heat is given to 5 g water, the rise in its temperature is [Specific heat of copper = 420 joule-kg-1 °C-1 , specific heat of water = 4200 joule-kg-I °C-1]
Which of the following substances (A, B and C) has the highest specific beat?
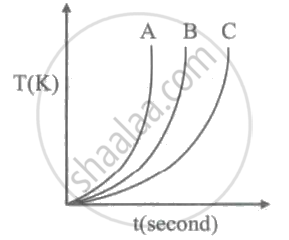
Which of the substances P, Q, or R has the lowest specific heat? The temperature v/s time graph is shown ______.

At same temperature and pressure of an ideal gas, ____________.
The ratio of the specific heats `c_"p"/c_"v"=gamma` in terms of degrees of freedom 'n' is given by ______.
Conductors have generally high specific heat capacities and insulators have low specific heat capacities.
A geyser heats water flowing at a rate of 2.0 kg per minute from 30°C to 70°C. If the geyser operates on a gas burner, the rate of combustion of fuel will be ______ g min-1.
[Heat of combustion = 8 × 103 Jg-1 Specific heat of water = 4.2 Jg-1°C-1]
