Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
| Shireen and Rafi are siblings aged five and six years respectively. They like to play at home pretending as king and queen. They wear their mother's gowns and decorate the chair like a throne. They believe that their toy horse is real and ride it. They want their mother to play with them and get upset when she refuses to play. They do not understand that their mother is tired and needs rest. |
- Name the stage of Cognitive Development that Shireen and Rafi are going through.
- Discuss any six features of the stage of Cognitive Development that Shireen and Rafi are experiencing.
उत्तर
- According to Jean Piaget, children between the ages of five and six are in the preoperational stage of cognitive development. At age five, children develop symbolic thinking, language abilities, and imagination, but struggle with logical reasoning and conservation principles. At age six, children gain verbal skills, creativity, and social relations, but struggle with logical reasoning and practical activities. These phases develop children's cognitive ability, problem-solving skills, and understanding of the environment.
- According to Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development, children typically enter the preoperational stage between the ages of two and seven. During this developmental period, children's cognitive abilities and reasoning processes are defined by several key characteristics. The preoperational stage has the following six characteristics:
- Symbolic Representation: Preoperational children use symbols such as words, pictures, and objects to represent non-existent things during symbolic play. During imaginative play, a child may use a block to represent a car.
- Self-centeredness: During the preoperational period, children exhibit egocentrism and struggle to understand that others may have different perspectives. Individuals who fail to consider others' perspectives often exhibit egocentric thinking.
- Centration: Centration refers to a child's pre-operational tendency to focus on one aspect of a situation and disregard others. This mental limitation may lead to poor decision-making and thinking. A toddler may focus on the height of a glass rather than its breadth when determining which holds more liquid.
- Lack of Conservation: Preoperational children sometimes lack the understanding of conservation, which states that an object's amount, volume, or mass remain constant despite physical changes. A young toddler may perceive a taller, narrower glass as carrying more liquid than a shorter, broader one, even if the quantities are the same.
- Animism: Animism refers to the belief that inanimate objects have human-like characteristics, desires, and feelings. In the preoperational stage, newborns can associate feelings or behaviors with objects. For instance, youngsters may believe the sun is "playing peek-a-boo" behind the clouds or that a plush animal is sad.
- Magical Thinking: Preoperational children often demonstrate magical thinking, a belief in irrational or supernatural cause-and-effect relationships. Individuals who believe their actions or ideas can influence outcomes may develop superstitious or fanciful beliefs.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer the following question briefly:
Who put forward the theory of moral development?
Answer the following question:
Briefly explain what is meant by gender identity.
Answer the following question briefly:
Explain the pre-conventional stage of morality.
Describe concrete cognitive development during childhood.
All individuals have a certain knowledge of themselves and some beliefs about their own characteristics. What is this known as?
In a study on Moral Development, subjects were presented with a hypothetical situation involving conflicting moral values or moral dilemmas. They were asked to make judgements on this situation and give their reasoning.
- Who proposed the Theory of Moral Development referred to above?
- Briefly explain each of the following stages of Moral Development:
- Obedience and Punishment Orientation.
- Good girl-Good boy Orientation.
- Social Contract Orientation/Legalistic Orientation.
Observe the image shown below and identify the stage of cognitive development.

Study the relation between the first two words and then fill in the fourth word.
Good boy-Good girl orientation : Conventional level : : Universal ethical principle orientation : ______.
| Ananta, aged 8 years and her sister Rashmi, aged 4 years, are given a set of objects like coloured marbles, toy animals and plastic fruits. They are asked to sort and classify these objects. Ananta can sort the objects based on colour, shape, and size easily. However, Rashmi cannot sort these objects based on their features. |
- According to Piaget’s theory, what stages of cognitive development are Ananta and Rashmi currently in? (2)
- Contrast the stages of cognitive development of Ananta and Rashmi on any two bases. (2)
|
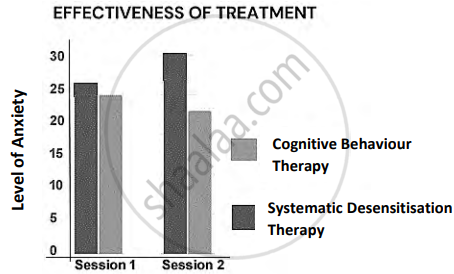
Ten participants, all having a phobia of spiders, were divided into two groups for a study that aimed at determining the effectiveness of Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) and Systematic Desensitisation. Each group underwent two sessions of each therapy. At the end of every session, the effectiveness of therapies was measured based on a questionnaire on Anxiety, which was filled by the participants. The responses of the participants have been depicted in the graph given below.
|
- Refer to the graph shown above and determine which treatment was more effective. Contrast the effectiveness of Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) and Systematic Desensitisation. (3)
- Discuss any two symptoms and any two causes of Phobias. (4)