Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
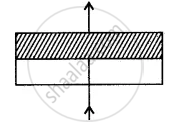
Show with the help of a ray diagram, the path of the ray when incident normally on the first surface of the glass block, through the block and the liquid.
उत्तर
We are assuming that the glass block is bounded by parallel plane refracting surfaces.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
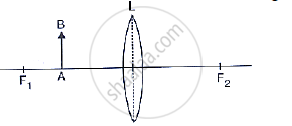
The following diagram shows an object AB and a converging lens L with foci F1 and F2. Draw two rays from the object AB and complete the diagram to locate the position of the image CD. Also mark on the diagram the position of eye from where the image can be viewed.
A lens forms an erect, magnified, and virtual image of an object. Where is the object placed in relation to the lens?
The focal length of a convex lens is 25 cm. At what distance from the optical centre of the lens an object be placed to obtain a virtual image of twice the size?
An illuminated object lies at a distance 1.0 m from a screen. A convex lens is used to form the image of the object on a screen placed at a distance of 75 cm from the lens. Find:
- the focal length of the lens, and
- the magnification.
What are conjugate foci?
How is the magnification (m) produced by a lens related to the object distance (u) and the image distance (v)?
Draw a neat diagram to explain the action of a convergent (convex) lens as a reading glass (or magnifying glass). State the characteristics of the image formed.
Copy and complete the following ray diagram.
An erect, magnified, and a virtual image is formed when an object is placed between the optical centre and principal focus of a lens.
(i) Name the lens.
(ii) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image with the above-stated characteristics.
Write an expression for the magnifying power of a simple microscope. How can it be increased?
