Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the 'Central dogma' as proposed by Francis Crick. Are there any exceptions to it? Support your answer with a reason and an example.
उत्तर
Francis Crick had proposed the 'Central Dogma', which states that the genetic information within a cell flows from DNA to RNA through transcription, and from RNA to proteins through translation.
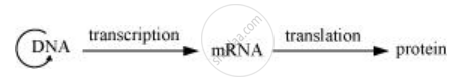
However, there are some exceptions to this process. In some viruses, the genetic material is in the form of RNA. In such cases, the direction of this information flow is reversed. The RNA is first converted into DNA through the process, reverse transcription. The DNA thus formed follow the usual path of the central dogma, i.e. it first converts into RNA, which is then translated into proteins. One such example of organism exhibiting reverse transcription is Influenza A virus.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer the following questions based on Hershey and Chases's experiments:
(a) Name the kind of virus they worked with and why?
(b) Why did they use two types of culture media to grow viruses in ? Explain.
(c) What was the need for using a blender and later a centrifuge during their experiments?
(d) State the conclusion drawn by them after the experiments.
Describe the Hershey and Chase experiment. Write the conclusion drawn by the scientists after their experiment.
Give reasons for the following:
The genetic code is 'universal'
Define Frameshift mutations
Explain how the biochemical characterisation (nature) of 'Transforming Principle' was determined, which was not defined from Griffth's experiments.
(a) Why did Hershey and Chase use radioactive 32P and 35S in their experiments? Explain.
(b) Following the experiments conducted by them, write what conclusion did they arrive at and how ?
Nucleotide arrangement in DNA can be seen by ______.
Identify the compound chemical structure is shown below. State any three of its physical properties.

Transformation was discovered by ______
Define transformation in Griffith's experiment. Discuss how it helps in the identification of DNA as the genetic material.
