Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State macroscopic form of Ohm’s law.
उत्तर
The macroscopic form of Ohm’s law is V = IR
Where V → Potential difference
I → Current
R → Resistance.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why are coils of electric toasters and electric irons made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
The relationship between the potential difference and the current in a conductor is stated in the form of a law.
1) Name the law.
2) What does the slope of V-I graph for a conductor represent?
3) Name the material used for making the connecting wire.
When a 12 V battery is connected across an unknown resistor, there is a current of 2.5 mA in the circuit. Calculate the value of the resistance of the resistor.
Calculate the electric field in a copper wire of cross-sectional area 2.0 mm2 carrying a current of 1 A.
The resistivity of copper = 1.7 × 10–8 Ω m
A wire has a length of 2.0 m and a resistance of 5.0 Ω. Find the electric field existing inside the wire if it carries a current of 10 A.
State the limitations of Ohm’s law.
A student carries out an experiment and plots the V-I graph of three samples of nichrome wire with resistances R1, R2 and R3 respectively. Which of the following is hue?
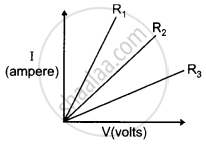
State Ohm’s law? How can it be verified experimentally? Does it hold good under all conditions? Comment.
Two cells of same emf E but internal resistance r1 and r2 are connected in series to an external resistor R (Figure). What should be the value of R so that the potential difference across the terminals of the first cell becomes zero.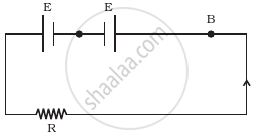
How is electric current related to the potential difference across the terminals of a conductor?
Draw a labelled circuit diagram to verify this relationship.
