Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the changes in the position, size and nature of the image when the object is brought from infinity up to the convex lens. Illustrate your answer by drawing ray diagrams.
उत्तर
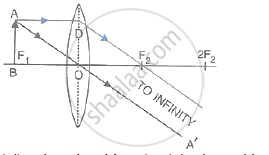
(i) When the object is situated at infinity, the position of image is at F2, it is very much diminished in size and it is real and inverted.
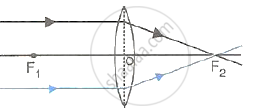
(ii) When the object (AB) is situated beyond 2F1, the position of image (A'B') is between F2 and 2F2, it is diminished in size and real and inverted.
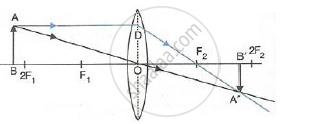
(iii) When the object (AB) is situated at 2F1, the position of image (A'B') is at 2F2, it is of same size as the object and real and inverted.
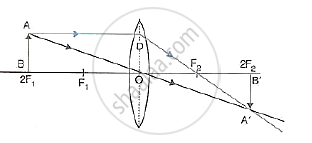
(iv) When the object (AB) is situated between 2F1 and F1, the position of image (A'B') is beyond 2F2, it is magnified in size and real and inverted.
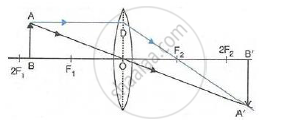
(v) When the object (AB) is situated at F1, the position of image is at infinity; it is very much magnified in size and real and inverted.
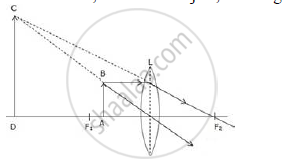
(vi) When the object (AB) is situated between lens and F1, the position of image (CD) is on the same side, behind the object; it is magnified in size and virtual and upright.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Rays of light incident parallel to the principal axis pass through the focus after reflection from a concave mirror.
The angle between the normal and refracted ray is called
Define the following terms :
Incident ray, Refracted ray, Angle of incidence, Angle of refraction.
What is a real image? Name the mirror which can be used to obtain the real image of an object. What should be the position of the object relative to the mirror?
A lens always forms an image between the object and the lens. State three characteristics of the image.
Distinguish between real and virtual image.
You can see your image in polished floors, but not in wooden table because ______.
The image formed by a pinhole camera is inverted because,
Magnification for the ______ image is always ______.
A concave lens produces only ______ image.
