Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the empirical laws of static and kinetic friction.
उत्तर
The empirical laws of friction are:
- Friction is independent of the surface of contact.
- The coefficient of kinetic friction is less than the coefficient of static friction.
- The direction of frictional force is always opposite to the motion of one body over the other.
- Frictional force always acts on the object parallel to the surface on which the object is placed,
- The magnitude of frictional force between any two bodies in contact is directly proportional to the normal reaction between them.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An object of mass m begins to move on the plane inclined at an angle θ. The coefficient of static friction of inclined surfaces is µs. The maximum static friction experienced by the mass is ______
A long stick rests on the surface. A person standing 10 m away from the stick. With what minimum speed an object of mass 0.5 kg should he has thrown so that it hits the stick. (Assume the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.7).
People often say “For every action, there is an equivalent opposite reaction”. Here they meant ‘action of a human’. Is it correct to apply Newton’s third law to human actions? What is mean by ‘action’ in Newton's third law? Give your arguments based on Newton’s laws.
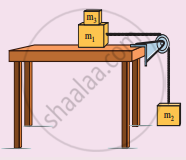
Two masses m1 and m2 are connected with a string passing over a frictionless pulley fixed at the comer of the table as shown in the figure. The coefficient of static friction of mass m1 with the table is µs Calculate the minimum mass m3 that may be placed on m1 to prevent it from sliding. Check if m1 = 15 kg, m2 = 10 kg, m3 = 25 and µs = 0.2.
A uniform metal chain is placed on a rough table such that one end of the chain hangs down over the edge of the table. When two-thirds of its chain length hangs over the edge the chain start sliding. Then the coefficient of static friction is:
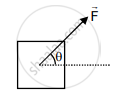
A block of mass m slides along a floor while a force of magnitude F is applied to it at an angle θ as shown in figure. The coefficient of kinetic friction is µK. Then, the block's acceleration 'a' is given by ______.
(g is acceleration due to gravity)
A uniform chain of length 3 metres and mass 3 kg overhangs a smooth table with 2 metres laying on the table. If k is the kinetic energy of the chain in joule as it completely slips off the table, then the value of k is ______.
(Take g = 10 m/s2)
A 40 kg wooden crate is being pushed across a wooden floor with a force of 160 N. If µk = 0.3, the acceleration of the crate is ______ m/s2. (g = 10 m/s2}
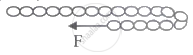
A chain of mass 'M' and length 'L' is put on a rough horizontal surface and is pulled by constant horizontal force 'F' as shown in the figure. The velocity of the chain as it turns completely ______.
(Coefficient of friction = μ)
Starting from rest, a body slides down a 45° inclined plane in twice the time it takes to slide down the same distance in the absence of friction. The coefficient of friction between the body and the inclined plane is ______.
