Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the two kinds of spherical mirror and distinguish them with the aid of proper diagrams.
उत्तर
The kinds of SPHERICAL MIRRORS are :
- CONCAVE MIRROR
- CONVEX MIRROR

CONCAVE MIRROR: Silvered surface is away from the centre of curvature and focal length is negative, i.e. reflecting surface is towards the centre of curvature.
CONVEX MIRROR: Silvered surface is towards the centre of curvature and focal length is positive i.e. reflecting surface is away from the centre of curvature. It always forms diminished (small) image which is VIRTUAL.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student focused the Sun rays using an optical device 'X' on a screen S as shown.

From this it may be concluded that the device 'X' is a (select the correct option)
(A) Convex lens of focal length 10 cm.
(B) Convex lens of radius of curvature 20 cm.
(C) Convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(D) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
Define the following term in the context of spherical mirrors:- Centre of curvature
An image that cannot be obtained on a screen is called ______.
Match the items given in Column I with one or more items of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | A plane mirror | (i) | Used as a magnifying glass. |
| (b) | A convex mirror | (ii) | Can form image of objects spread over a large area. |
| (c) | A convex lens | (iii) | Used by dentists to see enlarged image of teeth. |
| (d) | A concave mirror | (iv) | The image is always inverted and magnified. |
| (e) | A concave lens | (v) | The image is erect and of the same size as the object. |
| (vi) | The image is erect and smaller in size than the object. |
What happens when a ray of light falls normally (or perpendiculary) on the surface of a plane mirror?
State the kind of mirror used
(a) by a dentist, and
(b) as a street light reflector.
An object 5 cm high is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. Find the position and size of the image.
Define the term Principal axis.
Define focal length.
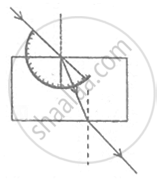
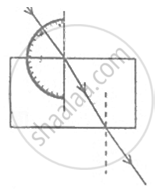
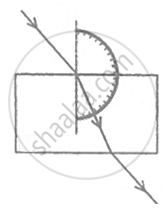
A student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular slab.
 |
 |
 |
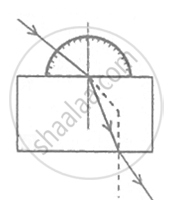 |
For measuring the angle of incidence, he must position the protractor in the manner shown in the figure:
