Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Temperature dependence of resistivity ρ(T) of semiconductors, insulators and metals is significantly based on the following factors:
- number of charge carriers can change with temperature T.
- time interval between two successive collisions can depend on T.
- length of material can be a function of T.
- mass of carriers is a function of T.
विकल्प
a and b
b and c
c and d
a and c
उत्तर
a and b
Explanation:
Resistivity is the intrinsic property of the substance. For a metallic conductor, resistivity is given by
`ρ = m/("ne"^2τ)`
Where n is the number of charge carriers per unit volume (number density) which can charge with temperature T and τ is relaxation time (time interval between two successive collisions) which decreases with the increase of temperature `(T oo 1/τ)`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
At room temperature (27.0°C) the resistance of a heating element is 100 Ω. What is the temperature of the element if the resistance is found to be 117 Ω, given that the temperature coefficient of the material of the resistor is 1.70 × 10−4 °C−1.
A heating element using nichrome connected to a 230 V supply draws an initial current of 3.2 A which settles after a few seconds to a steady value of 2.8 A. What is the steady temperature of the heating element if the room temperature is 27.0°C? The temperature coefficient of resistance of nichrome averaged over the temperature range involved is 1.70 × 10−4 °C−1.
As the temperature of a metallic resistor is increased, the product of its resistivity and conductivity ____________ .
Two resistors R and 2R are connected in series in an electric circuit. The thermal energy developed in R and 2R are in the ratio ______________ .
As temperature increases, the viscosity of liquids decreases considerably. Will this decrease the resistance of an electrolyte as the temperature increases?
Consider the following statements regarding a thermocouple.
(A) The neutral temperature does not depend on the temperature of the cold junction.
(B) The inversion temperature does not depend on the temperature of the cold junction.
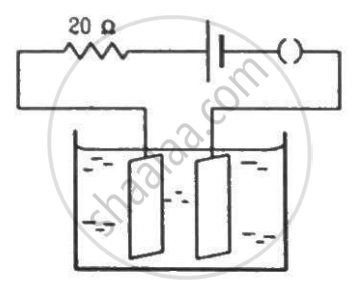
The figure shows an electrolyte of AgCl through which a current is passed. It is observed that 2.68 g of silver is deposited in 10 minutes on the cathode. Find the heat developed in the 20 Ω resistor during this period. Atomic weight of silver is 107.9 g/mol−1.
Find the thermo-emf developed in a copper-silver thermocouple when the junctions are kept at 0°C and 40°C. Use the data given in the following table.
| Metal with lead (Pb) |
a `mu V"/"^oC` |
b `muV"/("^oC)` |
| Aluminium | -0.47 | 0.003 |
| Bismuth | -43.7 | -0.47 |
| Copper | 2.76 | 0.012 |
| Gold | 2.90 | 0.0093 |
| Iron | 16.6 | -0.030 |
| Nickel | 19.1 | -0.030 |
| Platinum | -1.79 | -0.035 |
| Silver | 2.50 | 0.012 |
| Steel | 10.8 | -0.016 |
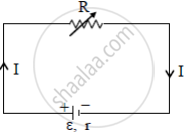
A variable resistor R is connected across a cell of emf ε and internal resistance r as shown in the figure. Draw a plot showing the variation of
(i) Terminal voltage V and
(ii) the current I, as a function of R.
By increasing the temperature, the specific resistance of a conductor and a semiconductor -
