Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The areas of pistons in a hydraulic machine are 5 cm2 and 625 cm2. What force on the smaller piston will support a load of 1250 N on the larger piston? State any assumption which you make in your calculation.
उत्तर
Area of small piston A1 = 5 cm2
Area of wider piston, A2 = 625 cm2
Force on small piston be F1
Force on wider piston or load, F2 = 1250 N
By the principle of hydraulic machine,
Pressure on narrow piston = pressure on wider piston
or, `F_1/A_1 = F_2/A_2`
or, `F_1/5 = 1250/625`
or, `F_1 = 1250/625 xx 5`
or `F_1 = 10` N
Assumption: No friction or leakage of liquid happens.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a simple diagram of a hydraulic jack and explain its working.
66640 Pa pressure is exerted by 0.50 m vertical column of a liquid. If g = 9.8 Nkg−1, calculate the density of the liquid.
Select the correct option.
One Pascal is equal to
Select the correct option.
The pressure exerted by 50 kg (g = 10 m/s−2) on an area of cross-section of 2 m2 is
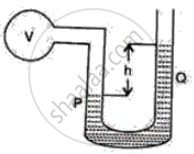
The following figure shows a manometer containing a liquid of density p. The limb P of the manometer is connected to a vessel V and the limb Q is open to atmosphere. The difference in the levels of liquid in the two limbs of the manometer is h as shown in the diagram. The atmospheric pressure is P0.
(i) What is the pressure on the liquid surface in the limb Q?
(ii) What is the pressure on the liquid surface in the limb P?
State Pascal's law.
State two applications of Pascal's law.
State two uses of a hydraulic press.
An iceberg of density 700 kg/m3 is floating in the water of density 1000 kg/m3. The percentage of the volume of ice cube outside the water is:
A hydraulic press can lift 100 kg when a mass 'm' is placed on the smaller piston. It can lift ______ kg when the diameter of the larger piston is increased by 4 times and that of the smaller piston is decreased by 4 times keeping the same mass 'm' on the smaller piston.
