Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The diagram below represents a process in plants. The setup was placed in bright sunlight. Answer the following questions:

a) Name the physiological process depicted in the diagram.
Why was oil added to the water?
b) When placed in bright sunlight for four hours, what do you observe with regard to the initial and final weight of the plant? Give a suitable reason for your answer
c) What happens to the level of water when this setup is placed in:
- Humid conditions?
- Windy conditions?
d) Mention any three adaptations found in plants to overcome the process mentioned in (i).
e) Explain the term ‘Guttation’.
उत्तर
a)
- Transpiration
- Oil was added to the water to prevent its evaporative loss.
b) Upon exposure to bright sunlight for four hours; the final weight will be lesser than the initial weight; because some water will be lost from the aerial parts of the plant by transpiration.
c)
- No change in the level of water
- The level of water drops.
d) The three adaptations found in plants to overcome transpiration are:
- Sunken stomata: The stomata may be sunken or covered by hairs (eg. Nerium)
- Narrow leaves: The leaves may become narrower to reduce surface area.
- Fewer stomata: The number of stomata may be reduced.
e) The leaves of certain plants exhibit droplets of water along their margins in the morning. This particularly happens in plants growing in warm humid conditions. A humid environment hampers transpiration while the roots continue to absorb water from the soil. This builds up a high hydrostatic pressure within the plant and “forces out” the excess water directly from the tips of veins in the leaf by a process called guttation.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A plant cell may burst when :
Explain Turgor pressure
Differentiate between the following:
Turgidity and Flaccidity
What is the difference between ‘flaccid’ and ‘turgid’? Give one example of flaccid condition in plants.
Give reason for the following:
A plant cell, when kept in a hypertonic salt solution for about 30 minutes, turns flaccid.
A leaf cell of a water plant was placed in a liquid other than pond water. After sometime, it assumed a shape as shown below:
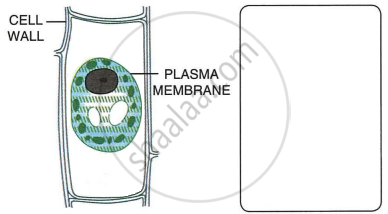
- Give the term for the state of the cell it has acquired.
- Name the structure which acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
- Comment on the nature (tonicity) of the liquid surrounding the cell.
- Name any one feature of this plant cell which is not present in an animal cell.
- Redraw in the space provided, the diagram of the cell if it is soon placed in ordinary water for some time.
Mention whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F) and give an explanation in support of your answer.
Soaked seeds burst into three seed coats.
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
Flaccidity is the reverse of turgidity.
Multiple Choice Question:
When cell is fully turgid, which of the following will be zero?
Addition of salt to pickles is a method of killing the bacteria by ______.
