Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The diagram given below represents a plant cell after being placed in a strong sugar solution. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:

- What is the state of the cell shown in the diagram?
- Name the structure that acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
- Label the parts numbered 1 to 4 in the diagram.
- How can the above cell be brought back to its original condition? Mention the scientific term for the recovery of the cell.
- State any two features of the above plant cell which is not present in animal cells.
उत्तर
- Plasmolysed cell
- Cell membrane acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
- 1 – Cell wall, 2 – Space filled with strong sugar solution, 3 – Plasma membrane, 4 – Nucleus
- If the cell is placed in a hypotonic sugar solution, the cell will be brought to its original condition. This is called deplasmolysis.
- Features present in the plant cell which are not present in the animal cell:
- Presence of cell wall.
- Ability to shrink the protoplasm and plasmolyse.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The state of a cell in which the cell wall is rigid and stretched by the increase in volume due to the absorption of water is called.
Give the equivalent terms for the following:
Loss of water through a cut stem.
Mention whether the following statement is true or false Correct the false statement by altering the last word only.
Cells that have lost their water content are said to be deplasmolysed.
Give suitable biological reasons for the following statement:
Root hairs become flaccid and droop when excess fertilizers are added to the moist soil around them.
Differentiate between:
Turgid and Flaccid.
Give Technical Term for the following.
The pressure exerted by cell contents on a plant cell wall.
Multiple Choice Question:
When cell is fully turgid, which of the following will be zero?
The hydrostatic pressure of the cell sap on the cell wall is called ______.
Addition of salt to pickles is a method of killing the bacteria by ______.
Given below is the figure of a plant cell showing different kinds of pressure acting upon it. Study the figure and answer the questions that follow:
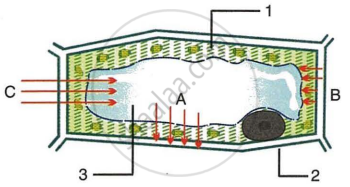
- In the figure, 1, 2 and 3 represent:
- Cytoplasm, Nucleus, Vacuole respectively
- Vacuole, Cytoplasm, Cell wall respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell membrane and vacuole respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell wall and Vacuole respectively.
- B in the figure represents:
- Osmotic pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Wall pressure
- Diffusion pressure
- A in the figure represents:
- irnbibition pressure
- Wall pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- C in the figure represents:
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- Wall pressure
- Imbibition pressure
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of a plasmolyzed plant cell.
