Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
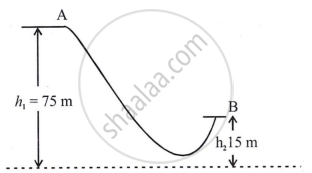
The diagram given below shows a ski jump. A skier weighing 60 kgf stands at A at the top of ski jump. He moves from A and takes off for his jump at B.

- Calculate the change in the gravitational potential energy of the skier between A and B.
- If 75% of the energy in part
- becomes kinetic energy at B.
- Calculate the speed at which the skier arrives at B. (Take g = 10 m s-2)
उत्तर
Force = weight of skier = 60 kgf = (60 × 10) N
∴ Mass of skier m = 60 kg
Height at A, h1 = 75 m; Height at B, h2 = 15 m
(a) ∴ Change in Gravitational potential energy between A and B = mgh
= mgh1 - mgh2
= mg [h1 - h2]
= 60 × 10 [75 - 15]
= 600 × 60
= 36000 J
= `36/10 xx 10000`
= 3.6 × 104 J
(b) 75 % of changes in energy = `(36000 xx 75)/100`
= 27000 J
which becomes K.E
∴ K.E. at B = 27000 J
`1/2 mv^2 = 27000`
`1/2 xx 60 v^2 = 27000`
∴ `v^2 = 27000/30`
= 900 J
12 V = `sqrt900`
= 30 ms-1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A metallic ball is hanging by a string from a fixed support. Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the forces acting on the ball and the string.
What is meant by the gravitational potential energy?
Two bodies of equal masses are placed at heights h and 2h. Find the ratio of their gravitational potential energies.
Find the gravitational potential energy of 1 kg mass kept at a height of 5 m above the ground. Calculate its kinetic energy when it falls and hits the ground. Take g = 10 m s-2.
Calculate the height through which a body of mass 0.5 kg is lifted if the energy spent in doing so is 1.0 J. Take g = 10 m s-2.
A man of mass 50 kg climbs up a ladder of height 15 m. Calculate:
- the work done by the man,
- the increase in his potential energy. (g = 9.8 m s-2)
A block A, whose weight is 100 N, is pulled up a slope of length 5 m by means of a constant force F (= 100 N) as illustrated in the following figure.
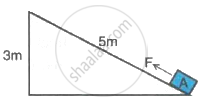
- What is the work done by force F in moving block A, 5 m along the slope?
- What is the increase in potential energy of the block A?
- Account for the difference in work done by the force and the increase in potential energy of the block.
Draw a graph of potential energy vs height for a body thrown vertically upwards. [Assume no friction is present.]
Write an expression for the potential energy of a body of mass m placed at a height h above the earth's surface. State the assumptions made, if any.
A box of mass 300 kg has gravitational potential energy stored in it equal to 29400 J. Find the height of the box above the ground. (Take g = 9·8 N kg-1).
