Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The diagram given below shows the internal structure of a spinal cord depicting a phenomenon. Study the diagram and answer the following questions.
 |
- Name the phenomenon shown in the figure and define the same.
- Identify the parts labelled as 1 and 2. Write one functional difference between these two.
- Name the bony protective covering and the membranous protective covering of the spinal cord.
- Label the guidelines 3 and 4.
- How is the labelled part 3 different from part 4 with respect to its composition (part of neuron)?
- Give the technical term for the point of contact between the two nerve cells.
- Name the fluid filled inside the central canal of spinal cord.
- Name the term used for a small gap between two neurons.
- Give one example of a neurotransmitter.
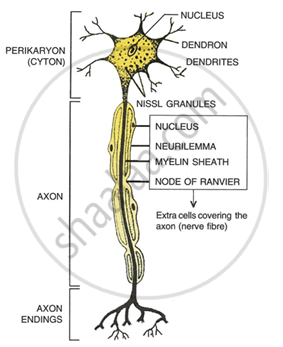
- Draw a neat diagram of a nerve cell and label the parts: Perikaryon, Node of Ranvier, Myelin sheath and Axon terminals.
उत्तर
- Reflex action: It is an automatic/quick/immediate, involuntary action in the body brought about by a stimulus.
-
- Sensory neuron: The neuron in the spinal cord receives nerve impulses via its axon/terminal ends, which connect to receptor cells.
- Motor neuron: It transmits impulses from the association neuron in the CNS to the effector organ (muscle or gland).
- The vertebral column protects the spinal cord, while the meninges (dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater) offer membrane protection.
- Part 3: Gray Matter,
Part 4: White Matter - Gray matter is made up of cell bodies (cytons), dendrites, and neutron synapses. White matter is made up of axons that connect nerve cells in gray matter.
- Synapse
- Cerebrospinal Fluid
- Synapse
- Acetylcholine
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
A neuron which carries an impulse to the brain is called a ........... neuron.
When you smell a favourite food your mouth begins to water (that is, you secrete saliva). Write down what is the example of the gland which is stimulated to secrete saliva.
Which of the following cannot be considered a receptor?
(a) ear
(b) nose
(c) muscle
(d) eye
The contraction of pupil of the eye in the presence of bright light is an example of :
(a) Voluntary reflex
(b) Spinal reflex
(c) Cerebral reflex
(d) Adrenal reflex
With the help of suitable example, describe reflex action.
Mention, if the following statement is True or False
A reflex action is a spontaneous response to a stimulus.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate Word
The control of reflex action is through:
Complete the following sentence with appropriate Word
Which of the following is not a natural reflex action?
Which sensory organ is involved in vertigo (sensation of oneself or objects spinning around)?
Categorise the following under stimulus and response.
Pain in the eye if something falls into it.
