Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The diagram shows a coil connected to a center zero galvanometerG . The galvanometer shows a deflect ion to the right when the north pole N of a powerful magnet is moved to the right as shown .
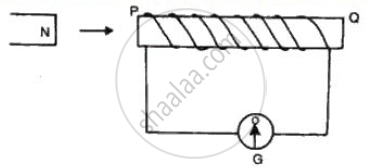
(i) Explain, why the defelct ion occurs in the galvanometer.
(ii ) State whether th e current in the coil is cl ockwise or anticl ockwise
when viewed from the end P.
(iii ) State th e observation in G when the coil is moved away from north
pole N of the magnet keeping the magnet stationary.
(iv)State the observation in G when both the coil and the magnet are
moved to right at th e same speed .
उत्तर
(i) This is due to change in magnetic flux in the coil. Due to change in magnetic flux an induced emf is produced in the coil. Hence, a current flows through the galvanometer.
(ii) The current appears anticlockwise when viewed from end A because end A will form north-pole.
(iii) The galvanometer now deflects towards left.
(iv) No deflection is observed as there is no relative motion between the magnet and the coil.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which quantity has the unit of watt?
Define kilowatt-hour.
An electric bulb is rated ‘100 W, 250 V’. How much current will the bulb draw if connected to a 250 V supply?
What is the resistance, under normal working conditions of a 240 V electric lamp rated at 60 W? If two such lamps are connected in series across a 240 V mains supply, explain why each one appears less bright.
An electric bulb marked 220 V, 100 W will get fused if it is made to consume 150 W or more. What voltage fluctuation will the bulb withstand?
Why is heating element wound on a long porcelain rod in a room heater.
What changes in energy occur in an electric heater?
What is ‘Rating’ of an electric appliance?
How can electric energy consumed by an electric appliance be calculated in kilowatt hour (kWh)?
A battery of e.m.f. 12V and internal resistance 1.6 Ω is connected to two resistors of 4Ω and 6Ω connected in parallel. Calculate:
(i) the current drawn from the battery,
(ii) the power dissipated in each resistor,
(ii)the total power supplied by the battery.
