Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The ejection of the photoelectron from the silver metal in the photoelectric effect experiment can be stopped by applying the voltage of 0.35 V when the radiation 256.7 nm is used. Calculate the work function for silver metal.
उत्तर
From the principle of conservation of energy, the energy of an incident photon (E) is equal to the sum of the work function (W0) of radiation and its kinetic energy (K.E) i.e.,
E = W0 + K.E
⇒ W0 = E – K.E
Energy of incident photon (E) = `("hc")/lambda`
Where,
c = velocity of radiation
h = Planck’s constant
λ = wavelength of radiation
Substituting the values in the given expression of E:
`"E" =((6.626 xx 10^(-34) " Js")(3.0xx10^8 " ms"^(-1)))/(256.7xx10^(-9) " m")`
`= 7.744 xx 10^(-19) " J"`
`= (7.744xx10^(-19))/(1.602xx10^(-19)) " ev"`
E = 4.83 eV
The potential applied to silver metal changes to kinetic energy (K.E) of the photoelectron. Hence,
K.E = 0.35 V
K.E = 0.35 eV
∴Work function, W0 = E – K.E
= 4.83 eV – 0.35 eV
= 4.48 eV
`(5lambda_0 - 2000)/(4lambda_0 - 2000) = (5.35/2.55)^2 = 28.6225/6.5025`
`(5lambda_0 - 2000)/(4lambda_0 - 2000) = 4.40177`
`17.6070lambda_0 - 5lambda_0= 8803.537 - 2000`
`lambda_0 = (6805.537)/(12.607)`
`lambda_0 = 539.8 " nm"`
`lambda_0 = 540 " nm"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find energy of each of the photons which correspond to light of frequency 3 × 1015 Hz.
Find energy of each of the photons which have the wavelength of 0.50 Å.
What is the number of photons of light with a wavelength of 4000 pm that provide 1 J of energy?
A photon of wavelength 4 × 10–7 m strikes on the metal surface, the work function of the metal being 2.13 eV. Calculate
- the energy of the photon (eV),
- the kinetic energy of the emission, and
- the velocity of the photoelectron (1 eV = 1.6020 × 10–19 J).
A 25-watt bulb emits monochromatic yellow light of the wavelength of 0.57μm. Calculate the rate of emission of quanta per second.
Electrons are emitted with zero velocity from a metal surface when it is exposed to radiation of wavelength 6800 Å. Calculate threshold frequency (v0) and work function (W0) of the metal.
Following results are observed when sodium metal is irradiated with different wavelengths. Calculate (a) threshold wavelength and, (b) Planck’s constant.
| λ (nm) | 500 | 450 | 400 |
| v × 10-5 (cm s-1) | 2.55 | 4.35 | 5.35 |
The electron energy in the hydrogen atom is given by En = (–2.18 × 10–18)/n2 J. Calculate the energy required to remove an electron completely from the n = 2 orbit. What is the longest wavelength of light in cm that can be used to cause this transition?
In astronomical observations, signals observed from the distant stars are generally weak. If the photon detector receives a total of 3.15 × 10–18 J from the radiations of 600 nm, calculate the number of photons received by the detector.
If travelling at same speeds, which of the following matter waves have the shortest wavelength?
Which of the following will not show deflection from the path on passing through an electric field?
A hypothetical electromagnetic wave is shown in Figure. Find out the wavelength of the radiation.
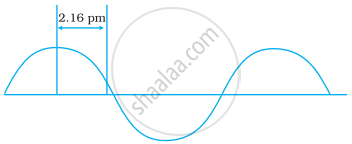
What is photoelectric effect? State the result of photoelectric effect experiment that could not be explained on the basis of laws of classical physics. Explain this effect on the basis of quantum theory of electromagnetic radiations.
