Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The following table shows the age distribution of head of the families in a certain country. Determine the third, fifth and eighth decile of the distribution graphically.
| Age of head of family (in years) |
Numbers (million) |
| Under 35 | 46 |
| 35 – 45 | 85 |
| 45 – 55 | 64 |
| 55 – 65 | 75 |
| 65 – 75 | 90 |
| 75 and Above | 40 |
उत्तर
To draw a ogive curve, we construct a less than cumulative frequency table as given below:
| Age of head of family (in years) |
Numbers (million) (f) |
Less than cumulative frequency (c.f.) |
| Under 35 | 46 | 46 |
| 35 – 45 | 85 | 131 |
| 45 – 55 | 64 | 195 |
| 55 – 65 | 75 | 270 |
| 65 – 75 | 90 | 360 |
| 75 and Above | 40 | 400 |
| Total | 400 |
Points to be plotted are (35, 46), (45, 131), (55, 195), (65, 270), (75, 360), (85, 400).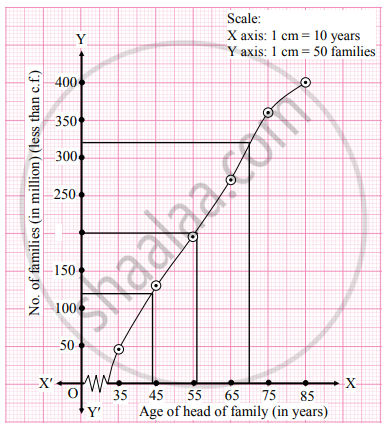
N = 400
For D3, we have to consider `(3"N")/(10)=(3(400))/(10)` = 120,
For D5, we have to consider `(5"N")/(10)=(5(400))/(10)` = 200
For D8, we have to consider `(8"N")/(10)=(8(400))/(10)` = 320
∴ We consider the values 120, 200, and 320 on Y-axis. From these points, we draw the lines parallel to X-axis. From the points where they intersect the less than ogive, we draw perpendiculars on the X-axis. The foot of the perpendicular represents the values of D3, D5, and D8.
∴ D3 ≈ 44, D5 ≈ 55.5, and D8 ≈ 70
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The following table gives frequency distribution of marks of 100 students in an examination.
| Marks | 15 –20 | 20 – 25 | 25 – 30 | 30 –35 | 35 – 40 | 40 – 45 | 45 – 50 |
| No. of students | 9 | 12 | 23 | 31 | 10 | 8 | 7 |
Determine D6, Q1, and P85 graphically.
The following table gives the distribution of daily wages of 500 families in a certain city.
| Daily wages | No. of families |
| Below 100 | 50 |
| 100 – 200 | 150 |
| 200 – 300 | 180 |
| 300 – 400 | 50 |
| 400 – 500 | 40 |
| 500 – 600 | 20 |
| 600 above | 10 |
Draw a ‘less than’ ogive for the above data. Determine the median income and obtain the limits of income of central 50% of the families.
The following frequency distribution shows the profit (in ₹) of shops in a particular area of city:
| Profit per shop (in ‘000) | No. of shops |
| 0 – 10 | 12 |
| 10 – 20 | 18 |
| 20 – 30 | 27 |
| 30 – 40 | 20 |
| 40 – 50 | 17 |
| 50 – 60 | 6 |
Find graphically The limits of middle 40% shops.
The following frequency distribution shows the profit (in ₹) of shops in a particular area of city:
| Profit per shop (in ‘000) | No. of shops |
| 0 – 10 | 12 |
| 10 – 20 | 18 |
| 20 – 30 | 27 |
| 30 – 40 | 20 |
| 40 – 50 | 17 |
| 50 – 60 | 6 |
Find graphically the number of shops having profile less than 35,000 rupees.
The following is the frequency distribution of overtime (per week) performed by various workers from a certain company.
Determine the values of D2, Q2, and P61 graphically.
| Overtime (in hours) |
Below 8 | 8 – 12 | 12 – 16 | 16 – 20 | 20 – 24 | 24 and above |
| No. of workers | 4 | 8 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 14 |
Draw ogive for the following data and hence find the values of D1, Q1, P40.
| Marks less than | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 |
| No. of students | 4 | 6 | 24 | 46 | 67 | 86 | 96 | 99 | 100 |
The following table gives the distribution of females in an Indian village. Determine the median age of graphically.
| Age group | No. of females (in ‘000) |
| 0 – 10 | 175 |
| 10 – 20 | 100 |
| 20 – 30 | 68 |
| 30 – 40 | 48 |
| 40 – 50 | 25 |
| 50 – 60 | 50 |
| 60 – 70 | 23 |
| 70 – 80 | 8 |
| 80 – 90 | 2 |
| 90 – 100 | 1 |
Draw ogive for the Following distribution and hence find graphically the limits of weight of middle 50% fishes.
| Weight of fishes (in gms) | 800 – 890 | 900 – 990 | 1000 – 1090 | 1100 – 1190 | 1200 – 1290 | 1300 –1390 | 1400 – 1490 |
| No. of fishes | 8 | 16 | 20 | 25 | 40 | 6 | 5 |
Find graphically the values of D3 and P65 for the data given below:
| I.Q of students | 60 – 69 | 70 – 79 | 80 – 89 | 90 – 99 | 100 – 109 | 110 – 119 | 120 – 129 |
| No. of students | 20 | 40 | 50 | 50 | 20 | 10 | 10 |
Determine graphically the value of median, D3, and P35 for the data given below:
| Class | 10 – 15 | 15 – 20 | 20 – 25 | 25 – 30 | 30 – 35 | 35 – 40 | 40 – 45 |
| Frequency | 8 | 14 | 8 | 25 | 15 | 14 | 6 |
The I.Q. test of 500 students of a college is as follows:
| I.Q. | 20 – 30 | 30 – 40 | 40 – 50 | 50 – 60 | 60 – 70 | 70 – 80 | 80 – 90 | 90 – 100 |
| Number of students | 41 | 52 | 64 | 180 | 67 | 45 | 40 | 11 |
Find graphically the number of students whose I.Q. is more than 55 graphically.
Draw a cumulative frequency curve more than type for the following data and hence locate Q1 and Q3. Also, find the number of workers with daily wages
(i) Between ₹ 170 and ₹ 260
(ii) less than ₹ 260
| Daily wages more than (₹) | 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 |
| No. of workers | 200 | 188 | 160 | 124 | 74 | 49 | 31 | 15 | 5 |
Draw ogive of both the types for the following frequency distribution and hence find median.
| Marks | 0 – 10 | 10 – 20 | 20 – 30 | 30 – 40 | 40 – 50 | 50 – 60 | 60 – 70 | 70 – 80 | 80 – 90 | 90 – 100 |
| No. of students | 5 | 5 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 15 | 10 | 8 | 5 | 2 |
