Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The lattice enthalpy of an ionic compound is the enthalpy when one mole of an ionic compound present in its gaseous state, dissociates into its ions. It is impossible to determine it directly by experiment. Suggest and explain an indirect method to measure lattice enthalpy of \[\ce{NaCl(s)}\].
उत्तर
The enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of an ionic compound dissociates into its ions in a gaseous state is called the lattice enthalpy of an ionic compound.
\[\ce{Ba^{+} + Cl- (s) -> Na+ (g) + Cl- (g)}\]
\[\ce{Δ_{lattice} H^Θ -> + 788 kJ mol^{-1}}\]
Let us now calculate the lattice enthalpy of \[\ce{Na+ Cl- (s)}\] by following steps given below:
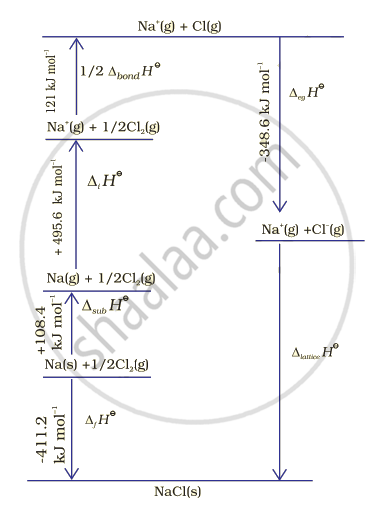
1. \[\ce{Na (s) -> Na (g)}\], sublimation of sodium metal, ΔsubHΘ = 108.4 KJmol-1
2. \[\ce{Na (g) → Na^{+} (g) + e- (g)}\] the ionization sodium atoms, ionization enthalpy.
ΔiHΘ = 496 kJ/mol
3. \[\ce{1/2 Cl2 (g) -> 2Cl (g)}\], the dissociation of chlorine, the reaction enthalpy is half the bond dissociation enthalpy.
\[\ce{1/2}\] Δbond HΘ = 121 kJ/mol
4. \[\ce{Cl (g) + e- -> Cl- (g)}\] electron gained by chlorine atoms. The electron gain enthalpy,
ΔegHΘ = – 348.6 kJ/mol.
5. \[\ce{Na+ (g) + Cl- (g) -> Na+ Cl- (s)}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The Born-Haber cycle for KCI is evaluated with the following data:
`Delta "H"_"f"^"o"` for KCl = - 436.7 kJ mol-1;
`Delta "H"_"f"^"o"` for K = 89.2 kJ mol-1
`Delta "H"_"ionization"^"o"` for K = 419.0 kJ mol-1 `Delta "H"_"ionization"^"o"` for Cl(g) = - 348.6 kJ mol-1
`Delta "H"_"bond"^"o"` for Cl2 = 243.0 kJ mol-1
The magnitude of lattice enthalpy of KCl in kJ mol-1 is ______. (Nearest integer)
The free energy change is ______ kJ mol-1 when 1 mole of NaCl is dissolved in water at 25°C. Lattice energy of NaCl = 777.8 kJ mol-1; ΔS for dissolution = 0.043 kJ mol-1; and hydration energy of NaCl = - 774.1 kJ mol-1.
The enthalpy of neutralisation of NH4OH with HCl is −51.46 kJ/mol−1 and the enthalpy of neutralisation of NaOH with HCl is −55.90 kJ/mol−1. The enthalpy of ionisation of NH4OH is ______.
