Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The north pole of a long bar magnet was pushed slowly into a short solenoid connected to a galvanometer. The magnet was held stationary for a few seconds with the north pole in the middle of the solenoid and then withdrawn rapidly. The maximum deflection of the galvanometer was observed when the magnet was ______.
विकल्प
moving towards the solenoid
moving into solenoid
at rest inside the solenoid
moving out of the solenoid
उत्तर
The north pole of a long bar magnet was pushed slowly into a short solenoid connected to a galvanometer. The magnet was held stationary for a few seconds with the north pole in the middle of the solenoid and then withdrawn rapidly. The maximum deflection of the galvanometer was observed when the magnet was moving out of the solenoid.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An electromagnet does not attract a piece of iron.
An electric bell has an electromagnet.
What is Maxwell's corkscrew rule? For what purpose is if used?
When the switch S is closed in the figure given below, the pointer of the galvanometer moves to the right.
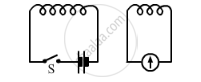
If S is kept closed, will the pointer:
(a) return to zero?
(b) stay over on the right?
(c) move to the left and stay there
(d) move to and fro until S is opened
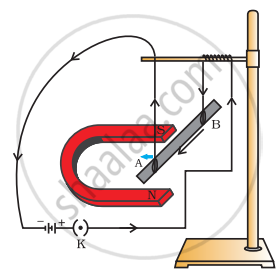
In the Activity shown below, how do we think the displacement of rod AB will be affected if
- current in rod AB is increased
- a stronger horse-shoe magnet is used
- length of the rod AB is increased?
|
What is the function of a split ring in an electric motor?
A uniform magnetic field exists in the plane of paper pointing from left to right as shown in Figure. In the field an electron and a proton move as shown. The electron and the proton experience

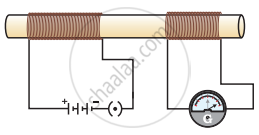
In the arrangement shown in Figure there are two coils wound on a non-conducting cylindrical rod. Initially the key is not inserted. Then the key is inserted and later removed. Then
Why do we cover plug pinholes which are within the reach of children with sellotape or a plastic cover when not in use?
Edison used a ______ wire coil is a vacuum glass and discovered the first electric bulb in 1879.