Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The resistance of a wire of 0.01 cm radius is 10 Ω. If the resistivity of the wire is 50 × 10-8 Ω, find the length of this wire.
उत्तर
Given, Radius, r = 0.01 cm = 0.0001 m
Resistance, R = 10 Ω
Resistivity, `rho = 50 xx 10^-8` Ω m
R = `rho "L"/"A"`
L = `"RA"/rho`
`= (10 xx 3.14 xx (0.0001)^2)/(50 xx 10^-8)`
= 0.628 m
Hence, the length of the wire is 0.628 m.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is (a) the highest, (b) the lowest total resistance that can be secured by combinations of four coils of resistance 4 Ω, 8 Ω, 12 Ω, 24 Ω?
Two conducting wires of the same material and of equal lengths and equal diameters are first connected in series and then parallel in a circuit across the same potential difference. The ratio of heat produced in series and parallel combinations would be:
What is the general name of the substances having infinitely high electrical resistance?
What happens to the resistance as the conductor is made thicker?
Calculate the resistance of a copper wire 1.0 km long and 0.50 mm diameter if the resistivity of copper is 1.7 × 10−8 Ω m.
How does the resistance of a conductor depend on:
length of the conductor?
The figure blow shows a variable resistor in a dimmer switch.
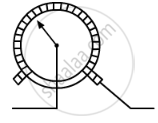
How would you turn the switch to make the lights: (a) brighter, and (b) dimmer? Explain your answer.
Write the relation between resistance and electrical resistivity of the material of a conductor in the shape of a cylinder of length `'l'` and area of cross-section `'A'` . Hence derive the S.I. unit of electrical resistivity.
Materials which allow larger currents to flow through them are called:
Assertion: Conductors allow the current to flow through themselves.
Reason: They have free charge carriers.
