Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The response of plants to gravity is known as geotropism. How are plant parts sensitive to gravity? Describe with the help of a diagram.
उत्तर
The response of plants to gravity can be observed in the laboratory when the seedlings are placed in a pot filled with moist soil.

Roots of plants show positive geotropism which means that they grow in the direction of gravity in the downward direction. This movement is good for the growth of the seedling. The roots need to grow downwards in the soil in search of water and minerals.
Shoots of plants show negative geotropism which means that they grow against the direction of gravity in the upward direction. This movement is beneficial for the elongation of the plant. The shoots need to grow upwards in the direction of sunlight so that the plant can grow in height.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
Give the scientific terms used to represent the Growing of roots towards the earth.
Name the five types of tropisms.
Which of the following is a growth movement and which is not?
- Folding up of leaves of sensitive plant on touching with hand.
- Folding up of petals of dandelion flower when light fades.
When the leaves of a Mimosa pudica plant are touched with a finger, they fold up quickly. This is an example of ______.
The shoot system grows upward in response to ______.
Roots of plants are:
Any change in the environment to which an organism responds is called ____________.
Assertion: Plants do have a nervous system for control and coordination.
Reason: Plants use electrochemical means to convey information from cell to cell.
The diagram given alongside shows a type of tropism. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
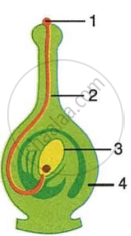
- Name and define the type of tropism shown in the diagram.
- Label the guidelines (1) to (4).
- Name two effective stimulants that help in the growth of part (2).
- Name two groups of plants where part (2) grows towards gametophyte with the help of the stimulants mentioned in (c).
