Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
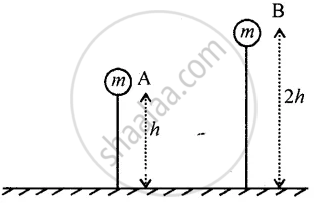
Two bodies of same masses are placed at heights h and 2h. Compare their gravitational potential energy.
उत्तर १
Gravitational pot. Energy of A: Gravitational pot.
energy of B = `(mgh)/(2mgh) = 1/2` = 1 : 2
उत्तर २
The gravitational potential energy (GPE) of an object is given by the formula:
GPE = mgh
Where:
- m = mass of the object
- g = acceleration due to gravity
- h = height of the object
For the two bodies:
-
First body at height h:
GPE1 = mgh -
Second body at height 2h:
GPE2 = mg (2h) = 2mgh
Ratio of their GPEs:
`(GPE_1)/(GPE_2) = (mgh)/(2mgh) = 1/2`
The gravitational potential energy of the second body is twice that of the first body. Thus, GPE2 : GPE1 = 2 : 1.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The potential energy of a freely falling object decreases progressively. Does this violate the law of conservation of energy? Why?
A body of mass m is moved from ground to a height h. If force of gravity on mass of 1 kg is g newton, find the potential energy stored in the body.
The gravitational potential energy stored in a box of weight 150 kgf is 1.5 × 104 J. Find the height of the box. Take 1 kgf = 10 N.
Define the term potential energy of a body.
The potential energy of a body is the energy by virtue of its ______.
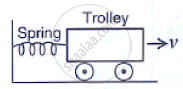
A spring is kept compressed by a small trolley of mass 0.5 kg lying on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the adjacent fig. When the trolley is released, it is found to move at a speed v = 2 m s-1. What potential energy did the spring possess when compressed?
A body falls freely under gravity from rest. Name the kind of energy it will possess at the point from where it falls.
A weightlifter is lifting weights of mass 200 kg up to a height of 2 metres. If g = 9.8 m s−2, calculate :
potential energy acquired by the weights.
A weightlifter is lifting weights of mass 200 kg up to a height of 2 metres. If g = 9.8 m s−2, calculate :
work done by the weightlifter
Give one example each of a body possessing : (i) kinetic energy, and (ii) potential energy.
