Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two genes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are linked. In a dihybrid cross involving these two genes, the F1 heterozygote is crossed with homozygous recessive parental type (aa bb). What would be the ratio of offspring in the next generation?
विकल्प
1 : 1 : 1: 1
9 : 3 : 3 : 1
3 : 1
1 : 1
उत्तर
1 : 1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is a dihybrid cross? How did Mendel perform this cross?
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
_______ is the ratio of dihybrid cross.
Under which conditions does the law of independent assortment hold good and why?
Name the seven contrasting traits of Mendel.
Define Genetics.
What are the reasons for Mendel’s successes in his breeding experiment?
Findings of Gregor Mendel were rediscovered by the following scientists EXCEPT for ______
A cross between two tall plants resulted in offspring having few dwarf plants. What would be the genotypes of both the parents?
Two linked genes a and b show 20% recombination. The individuals of a dihybrid cross between ++ /++ × ab/ab shall show gametes ______.
A dihybrid condition is ______.
In a dihybrid cross, F2 phenotypic ratio is 13 : 3. It is case of ______.
Mendel’s Law of independent assortment holds good for genes situated on the ______.
Assertion: When the two genes in a dihybrid cross are situated on the same chromosome, the proportion of parental gene combinations is much higher than the nonparental type.
Reason: Higher parental gene combinations can be attributed to crossing over between two genes.
Given below is a dihybrid cross performed on Drosophila.
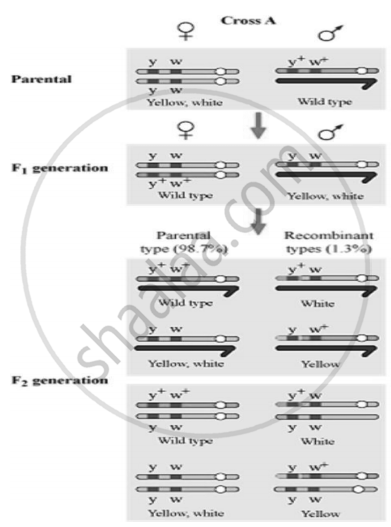
Which of the following conclusions can be drawn on the basis of this cross? When yellow bodied (y), white-eyed (w) Drosophila females were hybridized with brown bodied (y+), red-eyed males (w+) and F1 progenies were intercrossed, F2 generation would have shown the following ratio:
What is the difference between genetic drift and change due to natural selection?
Two pea plants - one with round yellow seeds (RRYY) and another with wrinkled green (rryy) seeds produce F1 progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds.
When F1 plants are self-pollinated, which new combination of characters is expected in F2 progeny? How many seeds with these new combinations of characters will be produced when a total 160 seeds are produced in F2 generation? Explain with reason.
Sahil performed an experiment to study the inheritance pattern of genes. He crossed tall pea plants (TT) with short pea plants (tt) and obtained all tall plants in F1 generation.
What will be set of genes present in the F1 generation?
Sahil performed an experiment to study the inheritance pattern of genes. He crossed tall pea plants (TT) with short pea plants (tt) and obtained all tall plants in F1 generation.
Give a reason why only tall plants are observed in F1 progeny.
Which one of the following genetic ratios will be obtained in a dihybrid test cross:
