Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two green plants are kept separately in oxygen-free containers, one in the dark and the other in continuous light. Which one will live longer? Give reasons.
उत्तर
As plants emit CO2 during breathing, plants kept under constant light survive longer. In the case of plants maintained in the dark, CO2 causes a shortage of oxygen, causing the plant to die sooner.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why is it necessary to excrete waste products?
The Biological/technical term for The removal of nitrogenous wastes from the body
Write the functions of the Urinary bladder
Differentiate between the following pair on the basis of what is indicated in the bracket.
Ureter and Urethra [function]
What do kidneys excrete?
Describe the mechanism of urine formation in human excretory system. Draw a labelled diagram to illustrate your answer.
Answer the following in short.
Define transpiration in plants.
Why is it necessary to maintain a normal osmotic concentration of the blood?
Given below is a simplified diagram of the human kidney cut open longitudinally. Answer the questions that follow.
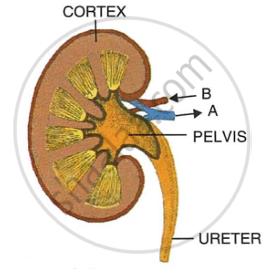 |
- Define excretion.
- Why does the cortex of the kidney show a dotted appearance?
- Why does the medulla of the kidney show a striped appearance?
- Write two differences in the composition of the blood flowing through the blood vessels 'A' and 'B'.
Choose the odd one out in the following serie:
Column of Bertini, minora calyces, brain.
Describe in brief how urine is produced in the human body.
Choose the Odd One Out:
The mode of excretion of nitrogenous wastes like ammonia which takes place by simple diffusion is called ______.
Bilirubin and Biliverdin are pigments which are ____________.
Elimination of nitrogenous wastes in the form of uric acid takes place in ____________.
Why is the rate of breathing in aquatic organisms much faster than in terrestrial organisms?
Given below is a list of substances - select the ones that need to be eliminated from the body.
Glucose, excess water, amino acids, urea, carbon dioxide, excess common salt, glycogen, uric acid.
An organ that produces urea:
