Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two short magnets of equal dipole moments M are fastened perpendicularly at their centre in the Figure . The magnitude of the magnetic field at a distance d from the centre on the bisector of the right angle is
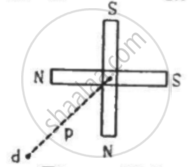
विकल्प
`(u_0)/(4pi) M/d^3`
`(u_0)/(4pi) (sqrt2M)/d^3`
`(u_0)/(4pi) (2sqrt2M)/d^3`
`(u_0)/(4pi) (2M)/d^3`
उत्तर
`(u_0)/(4pi) (2sqrt2M)/d^3`
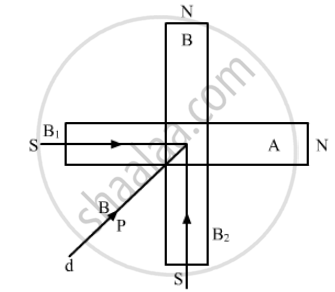
Magnetic field (B1) due to the short dipole A of dipole moment M at an axial point is given by,
`vec B_1 = (u_0)/(4pi) (2M)/d^3` ....(1)
Magnetic field (B2) due to the short dipole B of dipole moment M at an axial point is given by,
`vec B_2 = (u_0)/(4pi) (2M)/d^3` ....(2)
Resultant magnetic field (B) will be,
`B = sqrt (B_1^2 + B_2^2)`
B = `(u_0)/(4pi) (2sqrt2M)/d^3`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A circular coil of 300 turns and average area 5 * 10-3m2 carries a current of 15A. Calculate the magnitude of magnetic moment associated with the coil.
A charge 'q' is moved from a point A above a dipole of dipole moment 'p' to a point B below the dipole in equatorial plane without acceleration. Find the work done in the process.
Show that the orbital magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron is `(eVr)/2`
An electron in an atom revolves around the nucleus in an orbit of radius 0.53 Å. If the frequency of revolution of an electron is 9 x109 MHz, calculate the orbital angular momentum
[Given : Charge on an electron = 1.6 x 10–19 C; Gyromagnetic ratio = 8.8 x 1010 C/kg; π = 3.142]
The electron in the hydrogen atom is moving with a speed of 2.3x106 m/s in an orbit of radius 0.53 Å. Calculate the period of revolution of the electron. (Π = 3.142)
Do two distinct poles actually exist at two nearby points in a magnetic dipole?
A circular loop carrying a current is replaced by an equivalent magnetic dipole. A point on the axis of the loop is in
When a current in a circular loop is equivalently replaced by a magnetic dipole,
Let r be the distance of a point on the axis of a bar magnet from its centre. The magnetic field at such a point is proportional to
Let r be the distance of a point on the axis of a magnetic dipole from its centre. The magnetic field at such a point is proportional to
A magnetic dipole of magnetic moment 0.72 A m2 is placed horizontally with the north pole pointing towards south. Find the position of the neutral point if the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is 18 μT.
A monoenergetic (18 keV) electron beam initially in the horizontal direction is subjected to a horizontal magnetic field of 0.04 G normal to the initial direction. Estimate the up or down deflection of the beam over a distance of 30 cm (me = 9.11 × 10–31 kg).
The magnetic moment vectors µs and µl associated with the intrinsic spin angular momentum S and orbital angular momentum l, respectively, of an electron are predicted by quantum theory (and verified experimentally to a high accuracy) to be given by:
µs = –(e/m) S,
µl = –(e/2m) l
Which of these relations is in accordance with the result expected classically? Outline the derivation of the classical result.
The orbital speed of an electron orbiting around a nucleus in a circular orbit of radius 50 pm is 2.2 × 106 ms−1. Then the magnetic dipole moment of an electron is:
