Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Using the phenomenon of scattering of light, explain why there is a difference in the colour of the sun as it appears during sunrise and at noon.
उत्तर
During the sunrise, the sun is located near the horizon of the Earth. Hence, light has to travel a long distance through the Earth’s atmosphere. During sunrise, when the white sunlight falls on suspended atmospheric particles, blue colour light scatters out in deep space, while red colour light scatters less, and reaches the observer on the surface of the Earth. Hence, when this less scattered red light reaches our eyes, the sun and its surroundings appear to be reddish.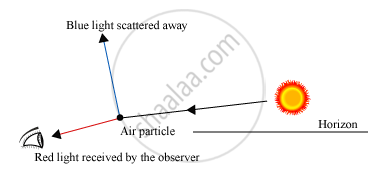
But at noon, when the sun is located overhead, the sun does not appear reddish in colour but it appears white. This is because light travels a relatively shorter distance when located overhead. Because of this reason, the scattering of blue, as well as red light, is much less when the sun is located overhead.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
With the help of scattering of light, explain the reason for the difference in colours of the Sun as it appears during sunset/sunrise and noon.
What information do we get about sunlight from the formation of a rainbow?
What did Newton demonstrate by his experiments with the prism?
What colours lie on the two sides of the 'green colour' in the spectrum of white light?
Which colour of the spectrum has
shortest wavelength?
Why does the sky appear dark (or black) to an astronaut instead of blue?
The colour of sky, in direction other than of the sun, is blue. Explain.
In white light of sun, maximum scattering by the air molecular present in the earth’s atmosphere is for ______.
Explain in brief the reason for the following :
Advanced sunrise
Which phenomenon is responsible for making the path of light visible?
