Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are enzyme inhibitors? Classify them on the basis of their mode of attachments on the active site of enzymes. With the help of diagrams explain how do inhibitors inhibit the enzymatic activity.
उत्तर
Enzymes are responsible to hold the substrate molecule for a chemical reaction and they provide functional groups which will attack the substrate to carry out the chemical reaction. Drugs which inhibit any of the two activities of enzymes are called enzyme inhibitors.
Enzyme inhibitors can block the binding site thereby preventing the binding of the substrate to the active site and hence inhibiting the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
Drugs Inhibit the attachment of natural substrate on the active site of enzymes in two different ways as explained below
(i) Drugs which compete with the natural substrate for their attachment on the active sites of enzymes are called competitive inhibitors.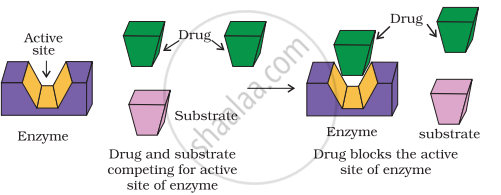
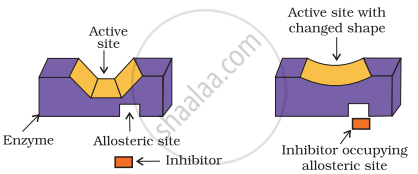
(ii) Some drugs bind to a different site of an enzyme called allosteric site. It changes the shape of the active site and substrate cannot recognize it. Such enzymes are called non-competitive inhibitor the bond formed between the enzyme and an inhibitor is strong covalent bond then enzyme is blocked permanently.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the macromolecules that are chosen as drug targets.
Which forces are involved in holding the drugs to the active site of enzymes?
Which of the following statements is correct?
Which of the following is not a target molecule for drug function in body?
Which of the following statements is not true about enzyme inhibitors?
Which site of an enzyme is called allosteric site?
What type of forces are involved in binding of substrate to the active site of enzyme?
Explain the role of allosteric site in enzyme inhibition?
Assertion: Enzymes have active sites that hold substrate molecule for a chemical reaction.
Reason: Drugs compete with natural substrate by attaching covalently to the active site of enzyme.
Assertion: Non-competitive inhibitor inhibits the catalyic activity of enzyme by binding with its active site.
Reason: Non-competitive inhibitor changes the shape of the active site in such a way that substrate can’t recognise it.
