Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are glycosidic linkages? In which type of biomolecules are they present?
उत्तर
The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharides are held together by a glycosidic linkage between C1 of α-glucose and C2 of β-fructose. Since the reducing groups of glucose and fructose are involved in glycosidic bond formation, between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage.
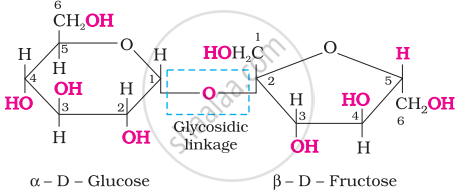
Sucrose
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Glucose or sucrose are soluble in water but cyclohexane or benzene (simple six membered ring compounds) are insoluble in water. Explain.
Write two main functions of carbohydrates in plants.
Classify the following into monosaccharides and disaccharides.
Ribose, 2-deoxyribose, maltose, galactose, fructose and lactose
What are the hydrolysis products of sucrose
The number of primary and secondary hydroxyl groups in ribose are -
(a) 1, 3
(b) 2, 3
(c) 3, 1
(d) 3, 2
Which of the following gives a positive Fehling solution test?
Glucose gives silver mirror test with Tollen’s reagent. It shows the presence of ____________.
The two functional groups present in a typical carbohydrate are:
Monosaccharides usually contains ____________ carbon atoms.
Which monosaccharide units are present in starch, cellulose and glucose and which linkages link these units?
