Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are n-type semiconductors? Why is the conductivity of doped n-type semiconductor higher than that of pure semiconductor? Explain with diagram.
उत्तर
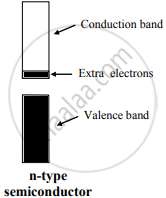
- An extrinsic semiconductor, which is obtained by adding group 15 element to an intrinsic semiconductor which belongs to group 14, is called an n-type semiconductor.
e.g. Silicon doped with phosphorus - n-type semiconductor contains an increased number of electrons in the conduction band.
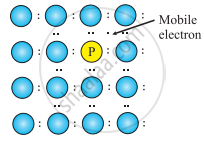
- Consider the doping of Si with phosphorus. Si has a crystal structure in which each Si atom is linked tetrahedrally to four other Si atoms. When a small quantity of phosphorous is added to pure Si, the P atoms occupy some vacant sites in the lattice in place of Si atoms. The overall crystal structure of Si remains unchanged.
Four of the five valence electrons of P are utilized in bonding the closest to four Si atoms. Thus, P has one extra electron than needed for bonding. Therefore, Si doped with P has more number of electrons in the conduction band than those in the conduction band in pure Si. Thus, the conductivity of Si-doped with P is higher than that of pure Si. The electrons in the conduction band move under the influence of an applied potential and conduct electricity.
P atom occupying regular site of Si atom
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
The following pictures show population of bands for materials having different electrical properties. Classify them as insulator, semiconductor or metal.
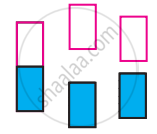
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
How does the electrical conductivity of a semiconductor change with temperature? Why?
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
The picture represents bands of MOs for Si. Label valence band, conduction band, and band gap.
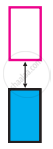
Answer the following in brief.
What are valence band and conduction band?
Distinguish with the help of diagrams metal conductors, insulators and semiconductors from each other.
Explain with diagram, Frenkel defect. What are the conditions for its formation? What is its effect on density and electrical neutrality of the crystal?
Which of the following is a metal?
What is band gap? Arrange band gaps in decreasing order for a semiconductor, metal conductor and insulator.
State the conditions for the formation of Schottky defect. The following picture shows bands for materials having different electrical properties.

Classify them as semiconductors, metals and insulators with reason.
Explain the classification of solids on the basis of electrical conductivity.
