Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are the changes seen in girls at the time of puberty?
उत्तर १
The changes seen in girls at the time of puberty are:
- Increase in breast size and darkening of the skin of the nipples present at the tips of the breasts.
- Appearance of hair in the genital area. Appearance of hair in other areas of skin like underarms, face, hands, and legs.
- Increase in the size of the uterus and ovary.
- Beginning of menstrual cycle.
- More secretion of oil from the skin, which results in the appearance of pimples.
उत्तर २
Girls at puberty develop hair in their armpits and around the pubic region. The mammary glands develop and become large. The hips get broadened and extra fat gets deposited on various parts of the body. The ovaries start releasing eggs; the vagina enlarges and menstruation starts.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What are sexually transmitted diseases?
State the exact location of the Proximal convoluted tubule.
State the main function of the Leydig cells
Write the names of male sex hormone?
The diagram shows female reproductive system. Name the parts labelled A to D.
(a) In which part do the sperms enter?
(b) Which part releases the egg?
(c) In which part does fertilisation take place?
(d) In which part does the foetus develop?

One of the following is not a part of the human male reproductive system. This is
(a) testis
(b) oviduct
(c) seminal vesicle
(d) prostrate gland
When a fertilised egg E formed in the oviduct of a human female divides repeatedly to form an embryo, the embryo gets implanted in the thick and soft lining of the uterus. After this a disc-like special tissue T develops between the uterus wall and embryo through which all the requirements of the developing embryo (and foetus) are met from the mother's body, The embryo is connected to the tissue T through a string like structure S.
(a) What is the other name of fertilised egg cell E?
(b) What is the name of tissue T?
(c) Name the string-like structure S.
(d) Name two substances which pass from mother's blood to embryo through tissue T and, one type of substance which passes from embryo to mother's blood.
(e) What happens to S when the baby is born? Why?
The germ cell A produced by a person X is round in shape and it fuses with another germ cell B having a long tail and produced by a person Y. The fusion of A and B produces a new cell C. The cell C divides repeatedly and grows inside the organ D of person X to form E in which the body features of the unborn baby are not much developed. E grows further to form F in which the various body features of the unborn baby (like hands, legs, head, eyes, and ears, etc.) can be identified. F grows further and ultimately forms a baby. What are A, B, C, D, E and F? Out of the two persons X and Y, which one is male and which one female?
Explain how the transmission of virus and bacteria diseases be prevented?
Draw a sectional view of human female reproductive system and label the following parts :
(i) Where the development of egg occurs.
(ii) Where fertilization takes place.
Give the names.
Any two sexual diseases.
Name the following:
Two accessory glands in the male reproductive system.
Define the following:
Parthenogenesis
Identify the given diagram.
Name the parts 1 to 5. 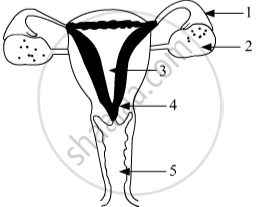
Answer the following question.
What is contraception? List three advantages of adopting contraceptive measures.
Choose the Odd One Out:
Choose the Odd One Out:
Mention the importance of the position of the testes in humans.
______ is a lytic enzyme released by the sperm.
During adolescence, reproductive phase starts and ______.
