Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are the different methods of contraception?
उत्तर
The contraceptive methods can be broadly divided into the following types:
- Natural method: It involves avoiding the chances of meeting sperm and ovum. In this method, the sexual act is avoided from day 10th to 17th of the menstrual cycle because during this period, ovulation is expected and therefore, the chances of fertilization are very high.
- Barrier method: In this method, the fertilization of ovum and sperm is prevented with the help of barriers. Barriers are available for both males and females. Condoms are barriers made of thin rubber that are used to cover penis in males and vagina in females.
- Oral contraceptives: In this method, tablets or drugs are taken orally. These contain small doses of hormones that prevent the release of eggs and thus fertilization cannot occur.
- Implants and surgical methods: Contraceptive devices such as the loop or Copper-T are placed in uterus to prevent pregnancy. Some surgical methods can also be used to block the gamete transfer. It includes the blocking of vas deferens to prevent the transfer of sperm, known as vasectomy. Similarly, the fallopian tubes of the female can be blocked so that the egg will not reach the uterus, known as tubectomy.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the process of development in human beings.
Why are testes located outside the abdominal cavity? What is responsible for bringing about changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty?
State the main function of the Leydig cells
A single highly coiled tube where sperms are stored gets concentrated, and mature is known as ______
Give biological explanations for The placenta is an important structure for the development of a foetus
Which part of the human body produces sperms?
Name the liquid that contains sperms.
Mention two functions of human ovaries.
What is gestation period? How much is the gestation period in humans?
What is ovulation? How often does it happen in human females?
In a flower, the parts that produce male and female gametes are respectively :
(a) sepal and anther
(b) filament and stigma
(c) anther and ovary
(d) stamen and style
The male gametes in a flower and in a human are produced respectively in :
(a) stigma and ovary
(b) anther and style
(c) ovary and testes
(d) anther and testes
When a fertilised egg E formed in the oviduct of a human female divides repeatedly to form an embryo, the embryo gets implanted in the thick and soft lining of the uterus. After this a disc-like special tissue T develops between the uterus wall and embryo through which all the requirements of the developing embryo (and foetus) are met from the mother's body, The embryo is connected to the tissue T through a string like structure S.
(a) What is the other name of fertilised egg cell E?
(b) What is the name of tissue T?
(c) Name the string-like structure S.
(d) Name two substances which pass from mother's blood to embryo through tissue T and, one type of substance which passes from embryo to mother's blood.
(e) What happens to S when the baby is born? Why?
When a female child is born, her ovaries already contain thousands of immature eggs (or ova) contained in immature structures A. On maturing, A bursts open and an egg shoots out of the ovary in a process called B. The process B starts in the females at puberty and occurs again and again after a time period x. Before every occurrence of process B, the inner lining of uterus becomes thick and soft with lots of blood vessels in it. When the egg cell gets fertilised by a sperm, then an event C occurs in the life of mature human female which lasts for time period y leading to the birth of baby. If, however, the egg cell released by the ovary does not get a sperm to fuse with, then the thick and soft inner lining of uterus breaks down and comes out of the female's body in an event called D. The occurrence of event D is controlled by chemical substances E.
(a) What are A?
(b) What is process B?
(c) What is the time period x?
(d) Name the event C.
(e) How much is the time period y?
(f) What is the name of process D?
(g) Name the chemical substances E.
Draw a sectional view of human female reproductive system and label the following parts :
(i) Where the development of egg occurs.
(ii) Where fertilization takes place.
Define the following:
Asexual reproduction
Define the following:
Clone
Identify the given diagram.
Name the parts 1 to 5. 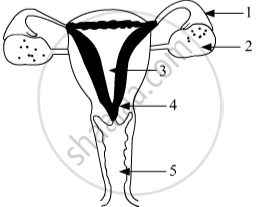
Name the Following
What does this abbreviation stand for LH?
