Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are the factors affecting the rate of enzyme reaction?
उत्तर
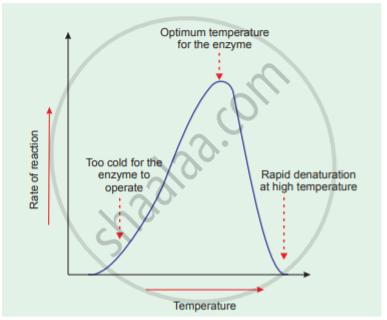
- Temperature: Heating increases molecular motion. Thus the molecules of the substrate and enzyme move more quickly resulting in a greater probability of occurrence of the reaction. The temperature that promotes maximum activity is referred to as optimum temperature.
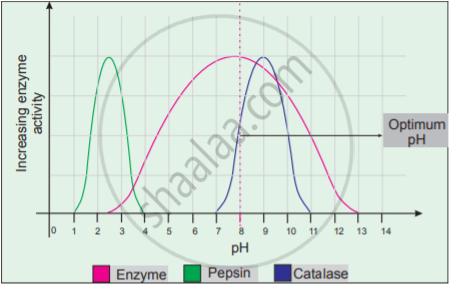
- pH: The optimum pH is that at which the maximum rate of reaction occurs. Thus the pH change leads to an alteration of enzyme shape, including the active site. If extremes of pH are encountered by an enzyme, then it will be denatured.
- Substrate Concentration: For a given enzyme concentration, the rate of an enzyme reaction increases with increasing substrate concentration.
- Enzyme Concentration: The rate of reaction is directly proportional to the enzyme concentration.

Rate of enzyme reaction
The Michaelis – Menton Constant (Km) and Its Significance:
When the initial rate of reaction of an enzyme is measured over a range of substrate concentrations (with a fixed amount of enzyme) and the results are plotted on a graph. With increasing substrate concentration, the velocity increases – rapidly at lower substrate concentrations. However, the rate increases progressively, above a certain concentration of the substrate the curve flattened out. No further increase in rate occurs. This shows that the enzyme is working at maximum velocity at this point. On the graph, this point of maximum velocity is shown as VMax.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which enzyme catalyzes following reaction?
OAA + acetyl-Co-A → Citrate + Co-A
Glycosidic bonds would be broken under the activity of which enzyme?
Study the following statements with respect to enzymes and select the correct option.
- Most of the enzymes work at an optimum temperature between 20°C and 35°C.
- Enzymes are destroyed at lower temperature of 10-20°C.
- Each enzyme exhibits its highest activity at a specific pH i.e. optimum pH.
Match the Column I (Enzymes) with Column II (Functions) and select the correct option:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| i. | Restriction endonuclease | a. | Joins the DNA fragments |
| ii. | Restriction exonuclease | b. | Extends primers on genomic DNA template |
| iii. | DNA ligase | c. | Cuts DNA at Specific position |
| iv. | Taq polymerase | d. | Removes nucleotides from the ends of DNA |
The enzymes get denatured ______.
The rate of enzyme reactions rises with the increase in substrate concentration. But it does NOT increase beyond a certain concentration because ______
Enzyme sucrase belongs to which one of the following classes?
Enzymes, vitamins and hormones can be classified into a single category of biological chemicals, because all of these ______.
Give the industrial applications of enzyme catalysis.
What are enzymes?
