Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are the factors that affect the frequency of a vibrating string and how do they affect the frequency?
उत्तर
The frequency (f) of a vibrating string is affected by:
(i) The length of the vibrating string. Frequency is inversely proportional to the length, i.e, `"f"α1/"l"`. it means, if length increases, frequency becomes less and if length decreases, frequency increases.
(ii) It is directly proportional to the square root of the tension, other factors remaining the same, e.g., if tension (or stretching force) is made 4 times, then the frequency will be `(sqrt4=2)` doubled.
(iii) The frequency, (f) is inversely proportional to the square root of the mass of unit length of the vibrating string, i.e., `"f"α1/sqrt"m′"` if m' is the mass of unit length of the string. Since m' = πr2.l, it shows that f is `α1/sqrt("r"^2)` or `1/"r"`, where r is the radius of the vibrating strings.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The adjacent diagram shows three different modes of vibrations P, Q and R of the same string.
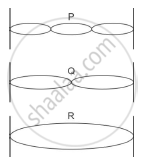
(i) Which vibration will produce a louder sound and why?
(ii) The sound of which string will have maximum shrillness?
(iii) State the ratio of wavelengths of P and R.
In following figure shows two tuning forks A and B of the same frequency mounted on two separate sound boxes with their open ends facing each other. The fork A is set into vibration.
- Describe your observation.
- State the principle illustrated by this experiment.

In following figure shows A, B , C and D represent test tube each of height 20 cm which are filled with water up to heights of 12 cm, 14 cm, 16cm and 18cm respectively. If a vibrating tuning fork is placed over the mouth if test tube D, a loud sound is heard.

- Describe the observations with the tubes A, B and C when the vibrating tuning fork is placed over the mouth of these tubes.
- Give the reason for your observation in each case.
- State the principle illustrated by the above experiment.
A tuning fork of frequency 256 Hz will resonate with another tuning fork of frequency:
(i) Define resonant vibrations.
(ii) Which characteristic of sound, makes it possible to recognize a person by his voice without seeing him?
A bucket kept under a running tap is getting filled with water. A person sitting at a distance is able to get an idea when the bucket is about to be filled.
(i) What change takes place in the sound to give this idea?
(ii) What causes the change in the sound?
Explain a tuning fork (vibrating) is held close to ear. One hears a faint sound. The same vibrating tuning fork is placed on table, such that its handle is in contact with table, one hears a loud sound.
