Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are the methods of measuring Elasticity of demand?
उत्तर
There are three methods of measuring the elasticity of demand.
- The percentage method:
Ep = `"ΔQ"/"ΔP"xx P/Q`
It is also known as the ratio method when we measure the ratio as
Ep = `"%ΔQ"/"%ΔP"`
% ∆Q = perCentage change in demand, %∆P = Percentage change in price.
- Total outlay method:
Marshall suggested that the simplest way to decide whether demand is elastic or inelastic is to examine the change in the total outlay of the consumer or total revenue of the firm.
Total revenue = Price × Quantity sold
TR = P × Q
Total outlay method:
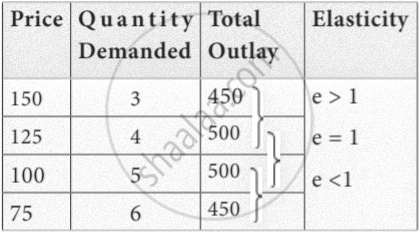
Demand is elastic if there is an inverse relationship between price and total outlay, and direct relation means inelastic. Elasticity is unity when the total outlay is constant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Demand for the commodity having multiple uses has elastic demand.
Explain the factors determining the elasticity of demand.
A consumer buys 18 units of a good at a price of Rs 9 per unit. The price elasticity of demand for the good is (–) 1. How many units the consumer will buy at a price of Rs 10 per unit? Calculate.
What will be the effect of 10 percent rise in price of a good on its demand if price elasticity of demand is (a) Zero, (b)-1, (c)-2.
A consumer spends Rs 100 on a good priced at Rs 4 per unit. When price rises by 50 percent, the consumer continues to spend Rs 100 on the good. Calculate the price elasticity of demand by percentage method
A consumer spends Rs 100 on a good priced at Rs 4 per unit. When its price falls by 25 percent, the consumer spends Rs 75 on the good. Calculate the price elasticity of demand by the Percentage method.
When the price of good rises from Rs10 to Rs12 per unit, its demand falls from 25 units to 20 units. What can you say about price elasticity of demand of the good through the 'expenditure approach'?
Define or explain the following concept.
Unitary elastic demand.
Give reasons or explain the following statements
Demand for basic necessities is inelastic.
What do you mean by a normal good?
Consider the demand curve D(p) = 10 − 3p. What is the elasticity at price `5/3` ?
State whether the following statement is TRUE and FALSE.
Perfectly inelastic demand curve is parallel to the X axis.
State whether the following statement is TRUE and FALSE.
Concept of Elasticity of Demand is useful for finance minister.
Give reason or explain the following statement:
Concept of Elasticity of Demand helps trade union leaders.
Arrange the following coefficients of price elasticity of demand in ascending order:
(−) 3.1, (−) 0.2, (−) 1.1
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
| Columns I | Columns II |
| (1) Perfectly elastic supply | (a) Es > 1 |
| (2) Perfectly inelastic supply | (b) Es < 1 |
| (3) Unitary elastic supply | (c) Es = 1 |
| (4) Relatively elastic supply | (d) Es = 0 |
Identify the correctly matched pair from the items in Column A by matching them to the items in column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Increase or decrease in demand for a commodity does not cause any change in its price. | (a) Effect on supply, in the case of Perfectly Elastic Demand. |
| 2. Increase or decrease in demand causes a change in the price of the commodity. Equilibrium quantity remains constant. | (b) Effect on demand, in the case of Perfectly Inelastic Supply. |
| 3. Increase or decrease in demand cause a change in the price of the commodity. Equilibrium quantity remains constant. | (c) Effect on demand, in the case of Perfectly Elastic Supply. |
| 4. Increase or decrease in demand for a commodity does not cause any change in its price. | (d) Effect on supply, in the case of Perfectly Elastic Demand. |
The elasticity of demand for school bag will be ______.
When is the demand for a good said to be elastic?
What is meant by elastic demand?
