Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are the various factors due to which the ionization enthalpy of the main group elements tends to decrease down a group?
उत्तर १
The factors responsible for the ionization enthalpy of the main group elements to decrease down a group are listed below:
- Increase in the atomic size of elements:
As we move down a group, the number of shells increases. As a result, the atomic size also increases gradually on moving down a group. As the distance of the valence electrons from the nucleus increases, the electrons are not held very strongly. Thus, they can be removed easily. Hence, on moving down a group, ionization energy decreases. - Increase in the shielding effect:
The number of inner shells of electrons increases on moving down a group. Therefore, the shielding of the valence electrons from the nucleus by the inner core electrons increases down a group. As a result, the valence electrons are not held very tightly by the nucleus. Hence, the energy required to remove a valence electron decreases down a group.
उत्तर २
Atomic size with the increase in atomic size, the number of electron shells increase. Therefore, the force that binds the electrons with the nucleus decreases. The ionization enthalpy thus decreases with the increase in atomic size.
Screening or shielding effect of inner shell electron. With the addition of new shells, the number of inner electron shells which shield the valence electrons increases. As a result, the force of attraction of the nucleus for the valence electrons further decreases and hence the ionization enthalpy decreases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Among the second period elements the actual ionization enthalpies are in the
order Li < B < Be < C < O < N < F < Ne.
Explain why Be has higher ΔiH than B?
Among the second period elements the actual ionization enthalpies are in the
order Li < B < Be < C < O < N < F < Ne.
Explain why O has lower ΔiH than N and F?
The first ionization enthalpy values (in kJmol–1) of group 13 elements are:-
| B | Al | Ga | In | Tl |
| 801 | 577 | 579 | 558 | 589 |
How would you explain this deviation from the general trend?
Would you expect the first ionization enthalpies for two isotopes of the same element to be the same or different? Justify your answer.
Which one of the following statements is incorrect in relation to ionization enthalpy?
Those elements impart colour to the flame on heating in it, the atoms of which require low energy for the ionisation (i.e., absorb energy in the visible region of spectrum). The elements of which of the following groups will impart colour to the flame?
(i) 2
(ii) 13
(iii) 1
(iv) 17
Among the elements \[\ce{B, Al, C}\] and \[\ce{Si}\], which element has the highest first ionisation enthalpy?
Nitrogen has positive electron gain enthalpy whereas oxygen has negative. However, oxygen has lower ionisation enthalpy than nitrogen. Explain.
Arrange the elements \[\ce{N, P, O}\] and \[\ce{S}\] in the order of increasing first ionisation enthalpy. Give reason for the arrangement assigned.
Explain the deviation in ionisation enthalpy of some elements from the general trend by using the given figure.
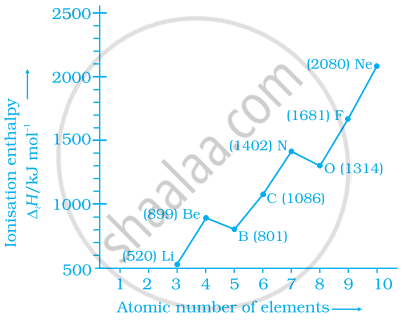
Explain the following:
Ionisation enthalpy decrease in a group from top to bottom?
Assertion (A): Generally, ionisation enthalpy increases from left to right in a period.
Reason (R): When successive electrons are added to the orbitals in the same principal quantum level, the shielding effect of inner core of electrons does not increase very much to compensate for the increased attraction of the electron to the nucleus.
Define ionisation enthalpy. Discuss the factors affecting ionisation enthalpy of the elements and its trends in the periodic table.
Discuss and compare the trend in ionisation enthalpy of the elements of group1 with those of group17 elements.
Consider the elements Mg, Al, S, P and Si, the correct increasing order of their first ionization enthalpy is ______.
For the gaseous reaction, \[\ce{K_{(g)} + F_{(g)} -> K^+_{ (g)} + F^-_{ (g)}}\], ΔH was calculated to be 19 kcal/mol under conditions where the cations and anions were prevented by electrostatic separation from combining with each other. The ionisation energy of K is 4.3 eV. The electron affinity of F is ______. (in eV)
