Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What do you expect the nature of hydrides is, if formed by elements of atomic numbers 15, 19, 23 and 44 with dihydrogen? Compare their behaviour towards the water.
उत्तर
The elements of atomic numbers 15, 19, 23, and 44 are phosphorus, potassium, vanadium, and ruthenium respectively.
- Hydride of phosphorus-
Hydride of nitrogen (PH3) is a covalent molecule. It is an electron-rich hydride owing to the presence of excess electrons as a lone pair on phosphorus.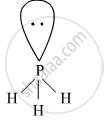
- Hydride of potassium-
Dihydrogen forms an ionic hydride with potassium owing to the high electropositive nature of potassium. It is crystalline and non-volatile in nature. - Hydrides of Vanadium and Ruthenium-
Both vanadium and ruthenium belong to the d–block of the periodic table. The metals of d–block form metallic or non–stoichiometric hydrides. Hydrides of vanadium and ruthenium are therefore, metallic in nature having a deficiency of hydrogen. - Behaviour of hydrides towards water-
Potassium hydride reacts violently with water as:
\[\ce{KH_{(s)} + H_2O_{(aq)} -> KOH_{(aq)} + H_{2(g)}}\]
Phosphorus (PH3) is a covalent hydride and slightly soluble in water.
Hydrides of vanadium and Ruthenium do not react with water. Hence, the increasing order of reactivity of the hydrides is (V, Ru) H < NH3 < KH.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Saline hydrides are known to react with water violently producing fire. Can CO2, a well-known fire extinguisher, be used in this case? Explain.
Arrange the following:
NaH, MgH2 and H2O in order of increasing reducing property.
How can saline hydrides remove traces of water from organic compounds?
Which of the following hydrides is electron-precise hydride?
Which of the following statements about hydrogen are correct?
(i) Hydrogen has three isotopes of which protium is the most common.
(ii) Hydrogen never acts as cation in ionic salts.
(iii) Hydrogen ion, \[\ce{H+}\], exists freely in solution.
(iv) Dihydrogen does not act as a reducing agent.
Which of the following statements is correct?
(i) Elements of group 15 form electron deficient hydrides.
(ii) All elements of group 14 form electron precise hydrides.
(iii) Electron precise hydrides have tetrahedral geometries.
(iv) Electron rich hydrides can act as Lewis acids.
NaH is an example of ______.
