Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What do you understand by ‘earthing’? What are the advantages of earthing in a household electric circuit? Explain, how it is done?
उत्तर
By earthing we mean that the metallic body of an electric appliance is connected to thick copper wire, which is buried deep in the earth and at its end is a copper plate surrounded by a mixture of charcoal and common salt.
Advantages: It is a kind of safety device which saves us from an electric shock, in a case when the
the metal casing of the appliance happens to touch the live wire or due to short-circuiting or leakage of electric current.
Whenever an appliance which is earthed, get short-circuited, the current from the metal casing of the appliance flows into the earth which acts as an ‘electric sink’, i.e., its potential always remains zero. Due to the flow of heavy current, the fuse in that circuit melts and disconnects the appliance from the circuit.
So the user who happens to touch the appliance is protected from receiving any electric shock. Another advantage is that overheating the house wiring system is saved from being damaged and the same time from being burnt out.
Procedure: A three core, cord having three wires coated with insulation of red, brown, and green colour, is used for connecting die appliance to the mains for drawing current from the mains. At one end of the cord, red is connected to the pin marked L (live), the brown to the pin marked N (neutral) and green to a thick pin of the plug. The three wires at the other end of the cord are connected to the appliance such that live and neutral wires are connected to the element and the earth wire is connected to the metal body of the appliance so as to earth it.
Once the plug is put in the socket, the current through the appliance becomes as soon as the switch is pressed. The live wire gets connected to the live wire of the mains. Neutral wire is connected to the neutral of the mains and the earth wire gets connected to the earth in the mains.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A 2 kWh heater, a 200 W TV and three 100 W lamps are all switched on from 6 p.m. to 10 p.m. What is the total cost at Rs 5.50 per kWh?
An electric heater of resistance 8 Ω takes a current of 15 A from the mains supply line. Calculate the rate at which heat is developed in the heater.
State the S.I. unit of electrical power.
A bulb marked 12 V, 24 W operated on a 12 volt battery for 20 minutes. Calculate:
(i) the current flowing through it, and
(ii) the energy consumed
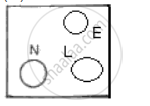
The diagram 31 shows a 3 terminal plug socket.
(i) What is the purpose of the terminal E?
(ii) To which part of the appliance is the terminal E connected?
(iii) To which wire L or N, is the fuse connected and why?
Household wiring for lamp connections can either be done in parallel or in series.Which one would you prefer? Give a reason for your answer.
How does the heat produced by die passage of current in a metallic wire depend on the time of passage of current in the wire?
An electric bulb is rated 240V-60W and is working at 100% efficiency.
(i) Calculate the resistance of bulb.
(ii) (a) Draw the circuit diagram.
(b) What is the rate of conversion of energy in each bulb?
(c) Total power used by the bulbs.
An electrical appliance is rated 1500 W, 250 V. This appliance is connected to 250 V mains. Calculate:
(i) the current drawn,
(ii) the electrical energy consumed in 60 hours,
(iii) the cost of electrical energy consumed at Rs. 2.50 per kWh.
The following table gives the electrical appliances used, their power and the average time for which they are used each day in a home. Estimate the monthly electricity bill if the rate is 60 paise per unit.
| Sr.no. | Name | Nos. | Power rating | Time/day |
| 1 | Bulb | 4 | 100 W | 7.5 hr |
| 2 | Fans | 2 | 50 W | 10 hr |
| 3 | T.V. | 1 | 100 W | 2 hr |
| 4 | Iron | 1 | 500 W | 1 hr |
| 5 | Electric stove | 1 | 750 W | 2 hr |
