Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What does the cerebellum of the brain control?
उत्तर
Cerebellum: It is the second-largest part of the brain and consists of two lateral hemispheres and a central vermis. It is composed of white matter with a thin layer of grey matter, the cortex. The white matter intermixes with the grey matter and shows a tree-like pattern called arborvitae. The surface of the cerebellum shows convolutions (gyri and sulci) a number of nuclei lie deep within each lateral or cerebellar hemisphere. Over 30 million neurons lie in the cortex. Three pairs of myelinated nerve bundles called cerebellar peduncles connect the cerebellum to the other parts of the CNS.
Functions: It is an important center that maintains the equilibrium of body, posture, balancing orientation, moderation of voluntary movements, maintenance of muscle tone. It is a regulatory center for neuromuscular activities and controls rapid activities like walking, running, speaking, etc. All activities of the cerebellum are involuntary (though may involve learning in early stages).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name two systems which taken together perform the functions of control and coordination in human beings.
Name the two types of coordination which take place in our body.
Name the three main parts of the human brain.
Fill in the blank:
The three main parts of the brain are ................................ and ............................
Name the parts (a) to (e) in the following diagram.
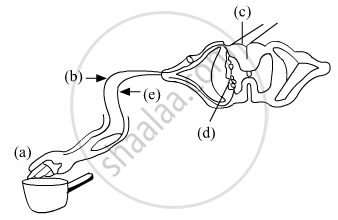
What is the term given to the sequence of events occurring in the diagram?
Explain the Term: Synapse
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word :
A nerve chain between a receptor and an effector organ is called _________.
Column ‘II’ is a list of items related to ideas in Column ‘I’. Match the term in Column ‘II’ with the suitable idea given in Column ‘I’.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Auditory canal | (a) | Channels pressure waves of air into the middle ear. |
| (ii) | Auditory (Eustachian tube) | (b) | Collects pressure waves of air. |
| (iii) | Auditory nerve | (c) | Converts pressure waves of air into vibrations of bone. |
| (iv) | Incus | (d) | Dissipates sound waves. |
| (v) | Malleus | (e) | Equalizes pressure between the middle ear and the atmosphere. |
| (vi) | Oval window | (f) | Provide information about the spatial orientation of the head. |
| (vii) | Pinna | (g) | Transfers vibrations from a bone to a fluid. |
| (viii) | Round window | (h) | Transfers vibrations from a bone to a membrane. |
| (ix) | Semi-circular canal | (i) | Transfers vibrations from a bone to a bone. |
| (x) | Stapes | (j) | Transfers vibrations from a membrane to a bone. |
| (xi) | Tympanic membrane | (k) | Transmits action potential to the auditory cortex. |
List out the functions of Endocrine system and Nervous system.
Pons helps in regulating respiration.
