Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
During prophase of mitosis, the chromatin fibres shorten and become thick to form chromosomes.
During metaphase, the chromosomes appear more distinct and clear and each consists of two parallel strands called chromatids joined by a centromere.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The diagram given below represents a certain stage of mitosis:
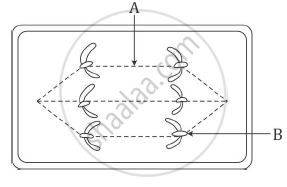
- Identify the stage of cell division.
- Name the parts labelled A and B.
- What is the unique feature observed in this stage?
- How many daughter cells are formed from this type of cell division?
Fill in the blank:
______ takes place in body cells resulting in growth and development.
Choose the correct answer:
Nuclear membrane reappears in ____________
The diagram below represents a certain stage of a cell.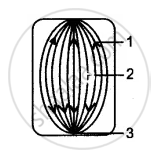
(i) Is it an animal cell or a plant cell ? Give one reason in support of your answer.
(ii) Label the parts numbered 1 – 3.
(iii) Which stage (phase) of mitosis is represented in this diagram
Give Technical Terms
The stage in mitosis when the nucleolus starts disappearing.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word :
Colchicine arrests cell division at __________.
Multiple Choice Question:
Karyokinesis is the division of
Multiple Choice Question:
The nuclear membrane disappears in
Column ‘II’ is a list of items related to ideas in Column ‘I’. Match the terms in Column ‘II’ with a suitable idea given in Column ‘I’.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Anaphase | (a) Chromosomes become arranged in a horizontal plane at the equator. |
| (ii) Prophase | (b) Daughter chromosomes move to opposite poles of the spindle. |
| (iii) Telophase | (c) Chromosomes become visible as fine, long threads. |
| (iv) Metaphase | (d) Chromosomes lose their distinctiveness and gradually become transformed into chromatin network. |
