Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is a lightning conductor? How does it work?
उत्तर
The conductor which is fixed on the top of the building to protect the buildings from the damage by lightning. The conductor consists of several sharp metal spikes connected to a thick copper strip. The other end of the copper strip is fixed to a metal plate buried inside the ground. The process is called earthing. The conductor works on the principle of induction. Whenever a charged cloud passes by the building, the conductor gets charge x opposite to that of the cloud
through the process of induction. Now, this acquired charge moves to the earth through the earthing system.
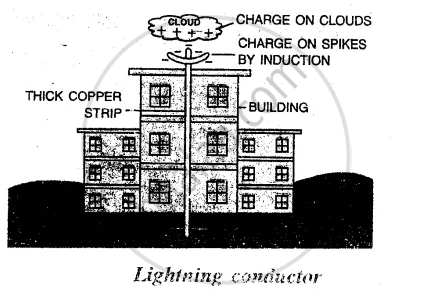
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Match the following
| Column A | Column B |
| Electric power | volt |
| kWh | joule |
| Electric current | volt × ampere |
| Electric energy | watt |
| watt | ampere |
| potential difference | electrical energy |
The cap of gold leaf electroscope is made of copper.
If a glass rod rubbed with silk is brought near the cap of a negatively charged electroscope, the divergence of leaves will decrease.
When an ebonite rod is rubbed with fur, the protons move from the ebonite rod to the fur.
Match the following
| Column A | Column B |
| A. Two like charges | 1 negative charge |
| B. Two unlike charges |
2 repel |
| C. Silver is a | 3 insulator |
| D. Silk is an | 4 attract |
| E. Ebonite rod rubbed with fur acquires | 5 conductor |
The factor responsible for charging a conductor is
An ebonite rod is rubbed with fur. Compare the charges acquired by them.
A glass rod is rubbed with silk. Explain the charging of the glass rod and the silk on the basis of electron movement.
An ebonite rod is rubbed with fur. Explain the charging of the ebonite rod and the fur on the basis of electron movement.
Name the two types of electroscopes.
