Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is long-sightedness? State the two causes of long-sightedness (or hypermetropia). With the help of ray diagrams, show:
(i) the eye-defect long-sightedness.
(ii) correction of long-sightedness by using a lens.
उत्तर
Long-sightedness, or hypermetropia, is a defect of vision because of which a person cannot see nearby objects clearly but has normal distant vision. Hypermetropia occurs because
1. the eye lens has low converging power, which causes the formation of the images of objects behind the retina, or
2. the eye ball is too short, which causes the formation of the images of objects behind the retina
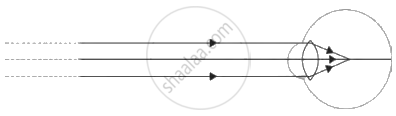
The ray diagram shows the hypermetropic eye and how the defect is corrected by using a convex lens, which converges the light rays from objects and forms clear images on the retina.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student is unable to see clearly the words written on the blackboard placed at a distance of approximately 4 m from him. Name the defect of vision the boy is suffering from. Explain the method of correcting this defect.
Draw ray diagram for the:-
(i) defect of vision and also
(ii) for its correction.
A student suffering from myopia is not able to see distinctly the objects placed beyond 5 m. List two possible reasons due to which this defect of vision may have arisen. With the help of ray diagrams, explain
(i) why the student is unable to see distinctly the objects placed beyond 5 m from his eyes.
(ii) the type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision and how this defect is corrected by the use of this lens.
(b) If, in this case, the numerical value of the focal length of the corrective lens is 5 m, find the power of the lens as per the new Cartesian sign convention
What is the other name of old age hypermetropia?
Name the defect of vision which can be corrected by a converging lens. Show clearly by a ray diagram how the lens corrects the defect.
Enumerate the common defects of vision, their causes and the possible methods of correcting them.
A person is unable to see objects distinctly placed within 50 cm from his eyes.
(a) Name the defect of vision the person is suffering from and list its two possible causes.
(b) Draw a ray diagram to show the defect in the above case.
(c) Mention the type of lens used by him for the correction of the defect and calculate its power. Assume that the near point for the normal eye is 25 cm.
(d) Draw a labeled diagram for the correction of the defect in the above case.
What type of lens is used to correct Hypermetropia?
In Myopia the human eye _______.
Observe the figure and answer the following questions:
- Name the defect of vision represented in the above figure.
- State the reasons for this defect.
- How is it corrected?
- Draw the diagram to show the correction of this defect.
