Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
| When a microorganism invades a host, a definite sequence of events usually occurs leading to infection and disease, causing suffering to the host. This process is called pathogenesis. Once a microorganism overcomes the defence system of the host, development of the disease follows a certain sequence of events as shown in the graph. Study the graph given below for the sequence of events leading to the appearance of a disease and answer the questions that follow: |
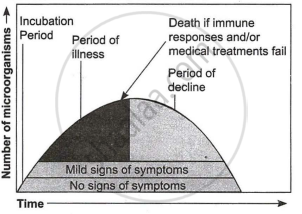
(a) In which period, according to the graph there are maximum chances of a person transmitting a disease/infection and why? (1)
(b) Study the graph and write what is an incubation period. Name a sexually transmitted disease that can be easily transmitted during this period. Name the specific type of lymphocytes that are attacked by the pathogen of this disease. (2)
OR
(b) Draw a schematic labelled diagram of an antibody. (2)
(c) In which period, the number of immune cells forming antibodies will be the highest in a person suffering from pneumonia? Name the immune cells that produce antibodies. (1)
उत्तर
(a) Period of illness: The number of disease-causing microorganisms reaches its maximum during the period of illness so, there are maximum chances of a person transmitting a disease/infection at this stage.
(b) The incubation period refers to the period from the absence of symptoms to the beginning of minor symptoms. The incubation period is the length of time between the introduction of germs and the onset of the first illness symptoms. For instance, chickenpox takes 14-16 days to incubate. The sexually transmitted illness that can spread during this time is AIDS. The pathogen in this disease targets a specific type of cell called a macrophage.
OR
(b)
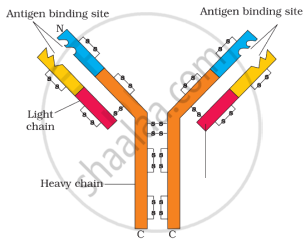
Structure of an antibody molecule
(c) In a person suffering from pneumonia, the number of immune cells forming antibodies will be at its highest during the period of illness. Antibodies are produced by B-lymphocytes.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name and explain the type of barriers which involve macrophages.
Which type of immunity is confered by colostrum secreted by mammary glands of mother during the initial days of lactation having abundant antibodies (lgA)?
Crypts of lieberkuhn are present in ______.
Which of the following acts as a physiological barrier to the entry of microorganisms into the human body?
Antibodies present in colostrum which protect the new born from certain diseases is of ______.
Give one difference between the following pair:
Sites of maturation of B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes
A patient was given an anti-retroviral drug by the doctor.
Mention any one symptom of HIV disease.
A patient was given an anti-retroviral drug by the doctor.
Give the scientific name of the causative agent of HIV disease
| Robert was suffering from chronic renal failure. At the doctors’ recommendation of transplantation of kidney received from a healthy donor, Robert underwent kidney transplant. However, after two weeks, the transplanted kidney was rejected by the immune system of Robert. |
- Identify and define the type of immune response that is responsible for the rejection of the grafted organ.
- Suggest a clinical method by which the rejection of the transplanted organ can be prevented.
Give example of active and passive immunity.
