Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When a ferromagnetic material goes through a hysteresis loop, the magnetic susceptibility
(a) has a fixed value
(b) may be zero
(c) may be infinity
(d) may be negative
उत्तर
(b) may be zero
(c) may be infinity
(d) may be negative
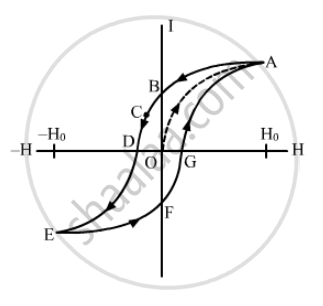
We know,
Magnetic susceptibility `=I/H`
At point B, the value of H is zero but I is non zero. Magnetic susceptibility is infinity here. At point C, value of magnetic susceptibility will be negative. Here Magnetic field is applied in opposite direction to reduce the intensity of magnetization to zero. The applied field to reduce the residual magnetization to zero is called coercivity. At point D, I is zero but H is not zero so susceptibility of the material will be zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When a ferromagnetic material goes through a hysteresis loop, its thermal energy is increased. Where does this energy come from?
A paramagnetic material is placed in a magnetic field. Consider the following statements:-
(A) If the magnetic field is increased, the magnetisation is increased.
(B) If the temperature is increased, the magnetisation is increased.
A paramagnetic material is kept in a magnetic field. The field is increased till the magnetisation becomes constant. If the temperature is now decreased, the magnetisation ___________ .
A ferromagnetic material is placed in an external magnetic field. The magnetic domains ______________ .
The permanent magnetic moment of the atoms of a material is not zero. The material ________________ .
The permanent magnetic moment of the atoms of a material is zero. The material _________________ .
A rod is inserted as the core in the current-carrying solenoid of the previous problem. (a) What is the magnetic intensity H at the centre? (b) If the magnetization I of the core is found to be 0.12 A m−1, find the susceptibility of the material of the rod. (c) Is the material paramagnetic, diamagnetic or ferromagnetic?
A dip circle is so set that its needle moves freely in the magnetic meridian. In this position, the angle of dip is 40º. Now the dip circle is rotated so that the plane in which the needle moves makes an angle of 30º with the magnetic meridian. In this position, the needle will dip by an angle ______.
The time period of oscillation of a magnet in a vibration magnetometer is 1.5 sec. The time period of oscillation of another magnet similar in size, shape and mass but having 1/4 magnetic moment than that of the 1st magnet oscillating at the same place will be ______.
The primary origin of magnetism lies in ______.
Which of the following is not showing the essential difference between electrostatic shielding by a conducting shell and magnetostatic shielding?
