Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When ones and three p orbitals hybridise,
विकल्प
four equivalent orbitals at 90° to each other will be formed
four equivalent orbitals at 109°28’ to each other will be formed
four equivalent orbitals, that are lying the same plane will be formed
none of these
उत्तर
four equivalent orbitals at 109°28’ to each other will be formed
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Identify the type of overlap present in H2. Explain diagrammatically.
Identify the type of overlap present in F2. Explain diagrammatically.
Complete the following Table.
| Molecule | Type of Hybridization | Type of bonds | Geometry | Bond angle |
| CH4 | - | 4C-H 4σ bonds |
Tetrahedral | - |
| NH3 | sp3 | 3N-H 3σ bonds 1 lone pair |
- | - |
| H2O | - | - | angular | 104.5° |
| BF3 | sp2 | - | - | 120° |
| C2H4 | - | - | - | 120° |
| BeF2 | - | 2 Be-F | Linear | - |
| C2H2 | sp | (3σ+2π) 1C-C σ 2C-H σ 2C-C π |
- | - |
According to Valence bond theory, a bond between two atoms is formed when ______.
In ClF3, NF3 and BF3 molecules the chlorine, nitrogen and boron atoms are ______.
Which of these represents the correct order of their increasing bond order.
XeF2 is isostructural with ______.
The overlap of orbitals involved in the formation of C - Br bond in vinyl bromide is ______.
Why does type of overlap given in the following figure not result in bond formation?
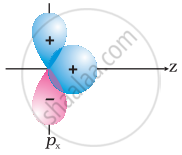 |
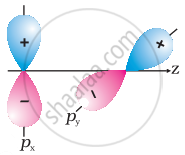 |
Briefly describe the valence bond theory of covalent bond formation by taking an example of hydrogen. How can you interpret energy changes taking place in the formation of dihydrogen?
