Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
(a) Why are thalassemia and haemophilia categorized as Mendelian disorders? Write the symptoms of these diseases. Explain their pattern of inheritance in humans.
(b) Write the genotypes of the normal parents producing a haemophilic son.
उत्तर
(a) Thalassaemia and haemophilia are categorised as Mendelian disorders because these are determined by alternation or mutation in a single gene.
Symptoms of thalassaemia: The main symptoms of thalassaemia are anaemia, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, cardiac enlargement and skeletal deformities.
Symptoms of haemophilia: Haemophilia is also called bleeder’s disease in which a single cut leads to non-stop bleeding. It prevents clotting of blood. A seriously affected person may bleed to death after even a minor skin cut.
Inheritance pattern of haemophilia:
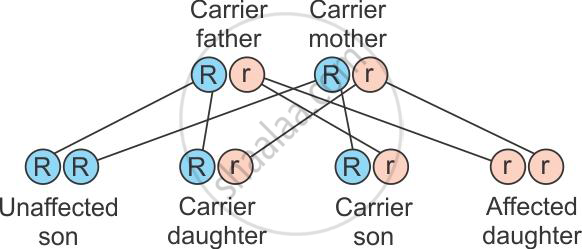
This is a sex-linked recessive disease which shows its transmission from an unaffected carrier female to some of the male progeny. It shows criss-cross inheritance. The heterozygous female (carrier) for haemophilia may transmit the disease to sons. The possibility of a female becoming a haemophilic is extremely rare because the mother of such a female would have to be at least a carrier and the father should be haemophilic.
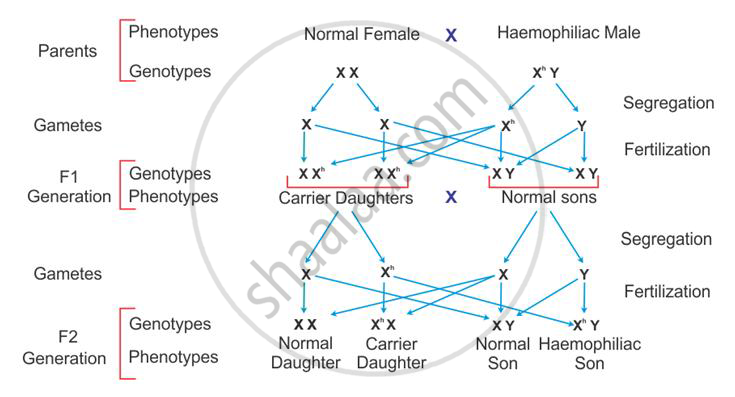
Inheritance pattern of thalassaemia:
Thalassaemia is an autosomal, recessively inherited blood disorder transmitted to the offspring when both parents are heterozygous. The defect arises because of either mutation or deletion which results in the reduced rate of synthesis of one of the globin chains of haemoglobin.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the scientific name of the fruit-fly. Why did Morgan prefer to work with fruit-flies for his experiments? State any three reasons.
In which of the following disorders number of chromosomes present is 47?
(A) Turner’s syndrome
(B) Cushing’s syndrome
(C) Acquired Immuno - Deficiency Syndrome
(D) Down’s syndrome
If a genetic disease is transferred from a phenotypically normal but carrier female to only some of the male progeny, the disease is ______.
In sickle cell anaemia glutamic acid is replaced by valine. Which one of the following triplets codes for valine?
The person with Turner’s syndrome has ______.
Failure of segregation of chromatids during cell division results in the gain or loss of chromosomes, this is called as ______.
“Genes contain the information that is required to express a particular trait.” Explain.
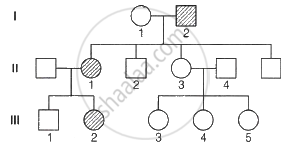
Fused ear lobes appear in the progeny due to an autosomal recessive gene. Work out the genotypes of number in the given pedigree.
Short stature in females, webbed neck absence of menstrual cycle and sterility are characteristics which of the following disease?
Jacob is genetically a carrier of the disorder that affects the shape of the RBCs, as shown in the diagram below. His son James suffers from the same disorder.

- Give the biochemical reason for the disorder that changes the shape of the RBCs, as shown above.
- Draw a Punnett square to show the genotype of the mother of James.
- Name and define the type of 'point mutation' responsible for this disorder.
