Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With the help of a labelled ray diagram, describe how a converging mirror can be used to give an enlarged upright image of an object.
उत्तर
A concave mirror gives an enlarged and upright image when an object is placed between the pole and the focus (object between P and F):
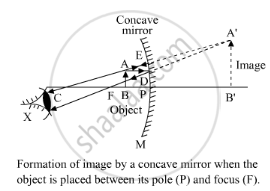
In the diagram, AB is the object and A'B' is the virtual and magnified image of AB.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student obtained a sharp image of a candle flame placed at the distant end of the laboratory table on a screen using a concave mirror to determine its focal length. The teacher suggested him to focus a distant building, about 1 km away from the laboratory, for getting more correct value of the focal length. In order to focus the distant building on the same screen, the student should slightly move the
(a) mirror away from the screen
(b) screen away from the mirror
(c) screen towards the mirror
(d) screen towards the building
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on a screen 48 cm in front of a mirror by keeping the flame at a distance of 12 cm from its pole.
(a) Suggest the type of mirror he should use.
(b) Find the linear magnification of the image produced.
(c) How far is the image from its object?
(d) Draw ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
If the focal length of a convex mirror is 25 cm, what is its radius of curvature?
The real image formed by a concave mirror is smaller than the object if the object is:
(a) between centre of curvature and focus
(b) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
(c) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
(d) at a distance equal to focal length
At what distance from a concave mirror focal length 10 cm should an object 2 cm long be placed in order to get an erect image 6 cm tall?
When an object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror, its image is formed at 10 cm in front of the mirror. Calculate the focal length of the mirror.
Name the lens which can concentrate sun's rays to a point and burn a hole in a piece of paper.
How can a concave mirror be used to obtain a virtual image of an object? Draw a diagram to illustrate your answer.
Match the following.
| Convex mirror | Radio telescopes |
| Parobolic mirror | Rear – view mirror |
| Snell’s law | Kaleidoscope |
| Dispersion of light | sin i/sin r =μ |
| Refractive index | Rainbow |
Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form an image larger than the actual object?
