Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write Explanatory answer.
State and explain the law of demand with its exception.
उत्तर
Meaning: -The Law of demand establishes the functional relationship between the Price of a commodity and the quantity of that commodity demanded at different prices, assuming other factors remaining constant.
When the price of a commodity rises, demand for it falls and when the price of the commodity falls, demand rises. So less quantity is demanded at higher prices and more quantity is demanded at lower prices. There exist inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded of a commodity.
Definition: -According to Marshall the law of demand, is defined as “Other things being equal, the quantity of a commodity demanded varies inversely with its price.”
Symbolically, the Law of demand can be expressed as follows:
Dx = f (Px)
Where, D = stands for the demand for commodity X
X stands for the commodity demanded
F stands for function of
Px stands for the price of the commodity X
We can explain this law with the help of a schedule and a diagram.
| Price (Rs.) | Quantity Demanded |
| 1 | 50 |
| 2 | 40 |
| 3 | 30 |
| 4 | 20 |
| 5 | 10 |
The Schedule shows that with an increase in Price the quantity demanded is decreasing. It indicates inverse relationship between the two variables price and quantity demanded. When the price is Re. 1 the consumer demand 50 units and when the price rises to Rs. 5 he demands the least that is 10 units.
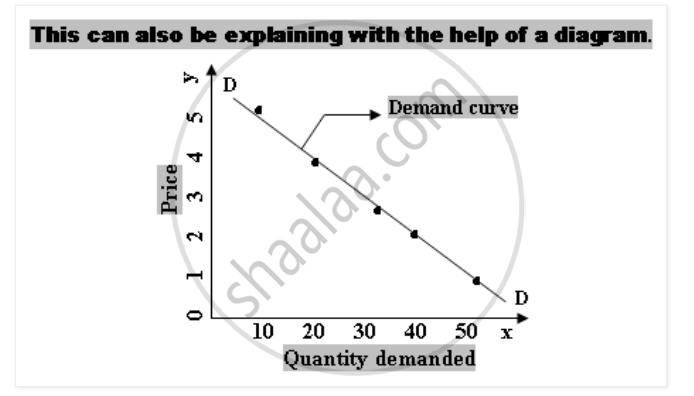
In the above diagram X-axis represents quantity demanded and Y-axis represents price. Various points from the schedule are plotted on the graph, joint those points we will be getting demand curve. DD is the demand curve which slopes downward from left to right indicating inverse relationship between price and Quantity demanded. This happens when the price is more, demand is less and when price is less, and demand is more.
- Giffen goods or inferior goods-Giffen Paradox: -Inferior goods are those goods whose demand does not rise even if their price falls. At times, the demand decrease, when the price of such gods falls. Sir Robert Giffen discovered this behaviour in England in relation to inferior goods such as bread. Therefore inferior goods are named after Giffen and they called ‘Giffen Goods’.
- Prestige Goods: There are certain goods and services, which represent ‘Status’ of ‘Prestige’for the people. Demand for these commodities is more when the price is more.
- Anticipation of changes in price: -If people anticipate a further rise in price, they may buy more at the existing higher price. Likewise, if people anticipating a further fall in price, they will not buy more even at the existing lower prices. They will wait for the price to fall further.
4. Price Illusion: -There is a belief among the people that the higher is the price, the better is the product and accordingly the greater is the demand for such goods.
- Changes in fashion: The law of demand may not work, if there is change in fashion. For example, if a product goes out of fashion and its price falls down, people will not buy more of it even at very low prices.
- Promotional activates: - Promotional activities such as advertising and salesmanship undertaken by seller can make the people buy more even at high prices.
- Changes in quality: if there is a change in the quality of the product, the law of demand may not apply. For instance, if there is improvement in quality of the product, some people my demand more even at higher price.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Demand for necessaries is................
(elastic / inelastic / infinitely elastic / unitary elastic)
Explain, with reasons, whether you Agree or Disagree with the following statement
There are no exceptions to the Law of Demand.
| Group 'A' | Group 'B' | ||
| a. | Pen and ink | 1 | Quantity-price |
| b. | Revenue | 2 | Accident |
| c. | Insurable risk | 3 | Transfer income |
| d. | Unemployment allowance | 4 | Short period |
| e. | Reverse repo rate | 5 | Long period |
| 6 | Change in demand | ||
| 7 | Joint demand | ||
| 8 | Quantity * price |
When does ‘decrease’ in demand take place?
What is meant by inelastic demand?
Explain the problem of what to produce.
Any statement above demand for a good is considered complete only when the following is/are mentioned in it. ( choose the correct alternative)
a) Price of the good
b) Quantity of good
c) Period of time
d) All of the above
If due to fall in the price of good X, demand for good Y rises, the two goods are : (Choose the correct alternative)
a. Substitutes
b. Complements
c. Not related
d. Competitive
Define or explain the following concept :
Effective demand .
Fill in the blank using proper alternative given in the bracket:
Perfectly inelastic demand curve is.....................................................
Fill in the blank with proper alternatives given in the bracket:
Indirect demand is also known as _______ demand.
Fill in the blank using proper alternatives given in the bracket:
Demand for salt is ...............
Answer the following question.
State and explain the law of demand.
Write whether the following statement is True or False:
Demand curve has a positive slope.
Write whether the following statement is True or False:
Salt has elastic demand.
Define or explain the concept of Demand schedule.
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given in the bracket:
The law of demand states ________ relation between demand and price.
fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given in the bracket:
Demand for salt is ___________.
State whether the following statement is TRUE and FALSE
When demand increases, the demand curve shifts to the left.
State whether the following statement is TRUE and FALSE
Law of demand is explained by Prof. Robbins.
Give reason or explain the following statement.
Increase in demand indicates a rightward shift in the demand curve.
Give reason or explain the following statement.
Demand curve slopes downward from left to right.
Give reason or explain the following statement.
Demand for factors of production is derived demand.
Do you agree with the following statement? Give reason
Many factors influence the demand for a commodity.
State whether the following statement is true or false. Give reasons for your answer :
X and Y are complementary goods. A fall in the price of Y will result in a rise in the price of X.
If the income of a consumer increases, discuss briefly its likely impact on the demand for a inferior good, Good X.
Choose the correct answer from given options
In the given figure X1Y1 and X2Y2 are Production Possibility Curves in two different periods T1 and T2 respectively for Good X and Good Y. A1 and A2 represent actual outputs and P1 and P2 represent potential outputs respectively in the two times periods.
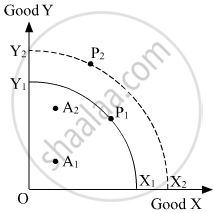
The change in actual output of Goods X and Y over the two periods would be represented by a movement from __________.
Answer the following question:
Elaborate the law of demand, with the help of a hypothetical schedule.
In case of ______ supply curve is a vertical straight line parallel to Y-axis.
Which of the following points relates to the transaction demand for money?
Law of demand states the ______ relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Which of the following points are related to the 'Paradox of Thrift'?
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (1) Utility | (a) Bread and butter |
| (2) Normal Goods | (b) Rise in price |
| (3) Contraction in demand | (c) Capacity of a commodity to satisfy human wants. |
| (4) Complementary goods | (d) Positively related |
If the increase in demand is greater than the increase in supply, then equilibrium price will ______
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (1) Budget Line | (a) Normal goods |
| (2) Bajra | (b) Inferior goods |
| (3) Consumer equilibrium | (c) Luxurious goods |
| (4) Elastic Demand | (d) M = Px*x + py*y |
Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following can cause an increase in demand:
Which of the following have elastic demand?
Which of the following statements is correct with respect to the correction of Excess Demand?
Which of the following is correct?
Read the following news report and answer the Q.97-Q.100 on the basis of the same:
The quantity of a commodity that a consumer is willing to buy and is able to afford, given the prices of goods and the consumer's tastes and preferences is called demand for the commodity. Whenever one or more of these variables change, the quantity of the good Chosen by the consumer is likely to change as well. The relation between the consumer's optimal choice of the quantity of a good and its price is very important and this relation is called the demand function. Thus, the consumer's demand function for a good gives the amount of the good that the consumer chooses at different levels of its price when the other things remain unchanged.
Assertion: The income of the consumers remains unchanged
Reason: Commodity should be a normal good.
Select the correct alternative from the following.
Which of the following statement is true?
The demand curve of a firm under monopoly is ______
Which of the following is the reason behind the downward slope of demand option?
Which of the following statements is true?
If there is no change in the demand for commodity X, even after a rise in its price, then its demand is ______
Read the case study and answer the questions 97 to 100:
The Coca-Cola Company is an American multinational beverage company, with its headquarters in Atlanta, Georgia. The first company that conducted its operation in the soft drink industry was Coca-Cola. It is the world's largest non-alcoholic beverage company serving more than 1.8 billion consumers daily in more than 200 countries. It has a portfolio of more than 3,500 (more than 800 no or low-calorie) products. However, the company is best known for its flagship product Coca-Cola which was originally intended to be a patented medicine invented in 1886 by pharmacist John Smith Pemberton in Columbus, Georgia. The Coca-Cola products can be termed as normal goods and in August 2019 Coca-Cola introduced a new product into the market, that is, zero sugar where the demand has increased for the product in the market.
According to the council of the Australian Food Technology Association and Institute of Food Science and Technology, the Australian nonalcoholic beverages industry has been growing steadily, with a 2.3 percent increase in overall production in the year 2000 which amounts to 2.25 billion liters. However, in the re~ent years, sales of customary carbonated soft drinks have dropped as more and more customers become health conscious and move away from high-calorie sugary drinks. Soft Carbonated drinks. and other alcohol-free beverage manufacturers have also sensed the effects of intensifying competition from private-label soft drink makers. Nevertheless, sales of greater value energy and sports drinks have driven profit generation in the industry.
______ is the want to buy a product backed by purchasing power.
Read the case study and answer the questions 97 to 100:
The Coca-Cola Company is an American multinational beverage company, with its headquarters in Atlanta, Georgia. The first company that conducted its operation in the soft drink industry was Coca-Cola. It is the world's largest non-alcoholic beverage company serving more than 1.8 billion consumers daily in more than 200 countries. It has a portfolio of more than 3,500 (more than 800 no or low-calorie) products. However, the company is best known for its flagship product Coca-Cola which was originally intended to be a patented medicine invented in 1886 by pharmacist John Smith Pemberton in Columbus, Georgia. The Coca-Cola products can be termed as normal goods and in August 2019 Coca-Cola introduced a new product into the market, that is, zero sugar where the demand has increased for the product in the market.
According to the council of the Australian Food Technology Association and Institute of Food Science and Technology, the Australian nonalcoholic beverages industry has been growing steadily, with a 2.3 percent increase in overall production in the year 2000 which amounts to 2.25 billion liters. However, in the re~ent years, sales of customary carbonated soft drinks have dropped as more and more customers become health conscious and move away from high-calorie sugary drinks. Soft Carbonated drinks. and other alcohol-free beverage manufacturers have also sensed the effects of intensifying competition from private-label soft drink makers. Nevertheless, sales of greater value energy and sports drinks have driven profit generation in the industry.
What has happened to the demand of zero sugar carbonated drinks?
Demand deposits include:
Which of the following statements is true?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow.
|
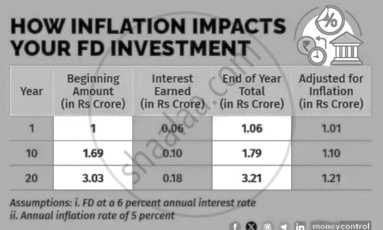
In India, Fixed deposits have long been a favourite investment choice of people, especially senior citizens, as it promise steady returns. It attracts those who are seeking a stable income. But it’s an illusion in the period of inflation. Inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, subsequently eroding the purchasing power of money. In simple terms, what money could buy today might not a few years down the line. Fixed deposits are financial instruments offered by banks where you deposit a lump sum amount for a fixed period at a predetermined rate of interest. Consider an investment of Rs 1 crore in a fixed deposit at a 6% annual interest rate and the annual rate of inflation is 5%. By the 10th year your pre inflation return is 1.79 crore, but post inflation it’s just 1.10 crore. The nominal value of investment in fixed deposits may appear to grow, inflation significantly diminishes their real value and purchasing power over time.
|
- What is the theme of the extract? (2)
- Differentiate between Demand pull and Cost push inflation. (2)
- What are the demand deposits and time deposits? (2)
- Since 1998 RBI has been using new measures of money supply, M0, M1, M2 and M3. Which one of these measures incorporates fixed deposit as one of its components? Mention the other components of that measure. (2)