Commerce (English Medium)
Science (English Medium)
Arts (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2021-2022
Date & Time: 9th December 2021, 11:30 am
Duration: 1h30m
Advertisements
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them:
- The question paper contains 60 questions out of which 50 questions are to be attempted. All questions carry equal marks.
- This questions paper consists of three Sections - Section A, B and C.
- Section - A contains 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions from Q. No. 1 to 24.
- Section - B contains 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions from Q. No. 25 to 48 wherein Q. No. 25 to 29 are MAP based question mandatory to attempt.
- Section - C contains 12 questions. Attempt any 10 questions from Q. No. 49 to 60 wherein Q. No. 49 to 52 are Source based questions mandatory to attempt.
- The first 20 Questions in Section - A, 20 questions in Section - B and 10 questions in Section - C attempted by a candidate will be evaluated.
- There is only one correct option for every Multiple Choice Question (MCQ). Marks will not be awarded for answering more than one option.
- There is no negative marking.
Which one of the following physical factor is responsible for the uneven distribution of population in India?
Availability of water
Agricultural development
Transport network
Urbanization
Chapter:
Which of the following group of countries, Indians mainly migrated in third wave of migration?
United States of America, Canada, United Kingdom
Japan, China, Vietnam
Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore
Mauritius, Fiji, Sri Lanka
Chapter:
Which of the following sectors has the highest percentage of working population in India?
Commerce
Agriculture
Manufacturing
Trade
Chapter:
Which of the following is the social consequence of migration?
Change in sex ratio
Remittances
Intermixing of cultures
Women empowerment
Growth of unplanned settlements
Increase in urban population
Depletion of ground water
Chapter: [0.02] Migration : Types, Causes and Consequences
In rural settlements people mainly depend on which of the following sectors for their livelihood?
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
Chapter:
Choose the characteristics of 'clustered settlements'?
Mainly found in Himachal Pradesh
Mainly found in lower valleys of the Himalayas.
Mainly found in Rajasthan.
Mainly found in fertile alluvial plains.
Chapter:
Which of the following is an example of 'modem town'?
Surat
Jaipur
Lucknow
Agra
Chapter:
Which one of the following is developed as the satellite town of Delhi?
Panipat
Rohtak
Mathura
Meerut
Chapter:
Which one of the following river comes under East Flowing Rivers of Group - 2?
Mahanadi
Godavari
Kaveri
Swarnarekha
Chapter:
Which of the following States has the highest percentage of irrigated area through wells and tube wells?
Punjab
Haryana
Uttar Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh
Chapter:
'Haryali Watershed Development Project' is run by which of the following?
Non-Governmental Organisation
Local Self Government
State Government
Central Government
Chapter:
In which one of the following States, Kund or Tanka is mainly used for rain water harvesting?
Rajasthan
Maharashtra
Andhra Pradesh
Gujarat
Chapter:
Which one of the following is often been described as transport network?
Respiratory system
Arteries of circulation
Blood circulation
Heart circulation
Chapter:
Who among the following defined Human Geography as - 'conception resulting from a more synthetic knowledge of the physical laws governing our earth and of the relations between the living beings which inhabit it'?
Ratzel
Ellen C. Semple
Paul Vidal de la Blache
Griffith Taylor
Chapter:
Which of the following school of thoughts is related to the different aspects of social wellbeing of the people?
Behaviouralistic
Humanistic
Radical
Utopian
Chapter:
Who among the following has said - 'Asia has many places where people are few and few place where people are very many'?
Prof. Amartya Sen
Dr. Mahbub-ul-Haq
George B. Cressey
Thomas Malthus
Chapter:
Choose the 'push factor' of migration from the followings:
Socio-economic backwardness
Pleasant climate
Security of life and property
Peace and stability
Chapter:
Which one of the following has played an important role to decline in death rate rapidly throughout the world?
Big Hospitals chain
Revolution in surgery
Medical help through insurance scheme
Inoculation against epidemics communicable diseases
Chapter:
Which is the main objective of development according to Nobel Laureate Amartya Sen?
Increase in brotherhood
Increase in freedom
Increase in democracy
Increase in equality
Chapter:
Which one of the following organisations proposed the 'Basic Needs Approach'?
International Labour Organisation
United Nations Development Programme
World Health Organisation
International Monetary Fund
Chapter:
Advertisements
Which one of the following countries comes under 'Medium level of Human Development'?
Norway
Canada
India
Singapore
Chapter:
Which one of the following activities comes under 'Primary Activities'?
Pastoralism
Weaving Basket
Milk Vending
Tailoring
Chapter:
Choose the physical factor affecting mining:
Demand of Mineral
Technological Knowledge
Infrastructural Development
Size of occurrence of the mineral deposits
Chapter:
Choose the feature of 'open-cast mining' from the followings:
Cheapest way of mining.
It requires lifts drills.
It requires ventilation system.
It has high labour cost.
Chapter:
Study the given map and answer the question that follows:
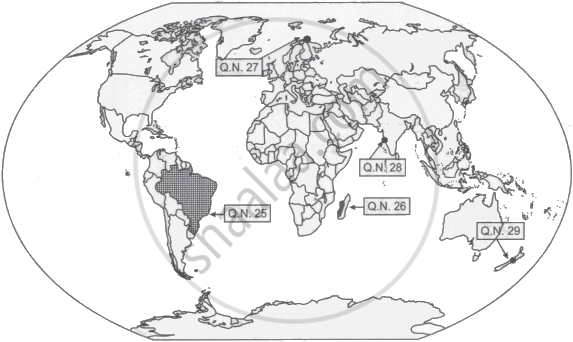
Choose the largest country (in terms of area) of South America Continent:
Argentina
Brazil
Chile
Panama
Chapter:
Study the given map and answer the question that follows:
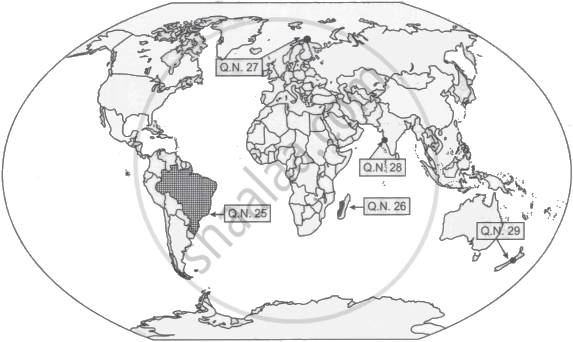
Which one of the following is an important area of nomadic herding?
Madagascar
Southern Africa
South Eastern Africa
Central Africa
Chapter:
Study the given map and answer the question that follows:

Choose the sea port of Europe:
Vancouver
Durban
North Cape
Belem
Chapter:
Study the given map and answer the question that follows:

Choose a mega city of the world:
Colombo
Perth
Islamabad
Mumbai
Chapter:
Study the given map and answer the question that follows:

Choose the major air port of New Zealand:
Perth
Johannesburg
Santiago
Auckland
Chapter:
Arrange the following approaches in ascending order on the basis of lime and choose the correct option.
- Areal differentiation
- Spatial organisation
- Exploration and description
- Regional analysis
I, II, III, IV
IV, III, II, I
III, IV, I, II
II, I, IV, III
Chapter:
Match the Column I with Column II and choose the correct option:
| Column - I (Sub-fields of Human Geography) |
Column - II (Interface with Sister Discipline of Social Science) |
| A. Behavioural Geography | i. Sociology |
| B. Cultural Geography | ii. Epidemiology |
| C. Gender Geography | iii. Psychology |
| D. Medical Geography | iv. Anthropology |
A - i, B - ii, C - iii, D - iv
A - iii, B - iv, C - i, D - ii
A - iv, B - iii, C - ii, D - i
A - ii, B - i, C - iv, C - iii
Chapter:
Which one of the following is the feature of 'plantation agriculture'?
It is a single crop specialisation.
It is multi crop specialisation.
It an example of subsistence agriculture.
Cultivation is done with the help of very primitive tools.
Chapter:
Which one of the following countries has officially proclaimed the Gross National Happiness (GNH) as the measure of the country's progress?
Nepal
Bhutan
Vietnam
Japan
Chapter:
Which of the following formula is correct to know the actual growth of population?
Birth + Death − in migration + out migration
Birth + Death + in migration − out migration
Birth − death − in migration + out migration
Birth − Death + in migration − out migration
Chapter:
Which one of the following continents has the highest population growth rate?
Asia
Europe
Africa
South America
Chapter:
Which one of the following is related to 'Kolkhoz'?
Co-operative farming
Collective farming
Truck farming
Garden farming
Chapter:
Choose the incorrect statement regarding commercial livestock rearing.
Commercial livestock rearing is associated with Western culture.
Parcels are fenced to regulate the grazing.
Move from one place to another depending on the amount of pastures.
When the grass of one parcel is grazed animals are moved to another parcel.
Chapter:
Which of the following pair is correct?
Mediterranean Agriculture - Production of citrus fruits
Mixed Farming - Paddy dominated cultivation
Primitive Subsistence Agriculture - Mechanised grain farming
Intensive Subsistence Agriculture - Jhuming farming
Chapter:
Study the following statements I and ll and choose the correct option.
- The decades 1951-1981 are referred to as the period of population explosion in India.
- During this period a rapid fall in the mortality rate and high fertility rate in the country.
Only I is correct.
Only II is correct.
I and II both are wrong.
I and II both are correct, II correctly explain the I.
Chapter:
Which one of the following countries has the highest immigration by the last residence in India?
Sri Lanka
Bangladesh
Pakistan
Nepal
Chapter:
Advertisements
Match the Column I with Column II and choose the correct option:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| I. Medieval town | A. Modinagar |
| ll. Mining town | B. Varanasi |
| iii. Industrial town | C. Jaipur |
| iv. Ancient town | D. Raniganj |
i - A, ii - B, iii - C, iv - D
i - B, ii - A, iii - D, iv - C
i - C, ii - D, iii - A, iv - B
i - D, ii - C, iii - B, iv - A
Chapter:
In India often females move out from their parental houses after marriage. Which one of the following States, the case is reverse?
Kerala
Karnataka
Meghalaya
Arunachal Pradesh
Chapter:
The main reason of intra migration in India is ______.
Employment
Education
Health
Pleasant Climate
Chapter:
In which one of the size classes has the highest number of towns in India?
I
II
III
IV
Chapter:
Choose the correct pair of the following:
Garrison town - Ambala
Tourist town - Saharanpur
Mining town - Kolkata
Administrative town - Singruali
Chapter:
Which one of the following is the most important objective of 'Smart City' Mission?
To develop road network
To expand the city
To provide sustainable environment
To provide employment opportunities
Chapter:
In which of the size class of urban centres India has the highest population?
I
II
III
IV
Chapter:
Which one of the following is the feature of 'National Water Policy'?
Should be least use of water.
Should be clean rivers.
Should be conserve water in each house.
Awareness as a scarce resource should be fostered.
Chapter:
Read the given source and answer the questions that follow:
|
Density of Population Density of population, is expressed as number of persons per unit area. It helps in getting a better understanding of the spatial distribution of population in relation to land. The density of population in India (2011) is 382 persons per sq. km. There has been a steady increase of more than 200 persons per sq. km over the last 50 years as the density of population increased from 117 persons/sq. km in 1951 to 382 persons/sq. km in 2011. Population densities in the country which ranges from as low as 17 persons per sq. km in Arunachal Pradesh to 11,297 persons in the National Capital Territory of Delhi. Among the Northern Indian States, Bihar (1102), West Bengal (1029) and Uttar Pradesh (828) have higher densities, while Kerala (859) and Tamil Nadu (555) have higher densities among the peninsular Indian States. States like Assam, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Jharkhand, Odisha have moderate densities. The hill states of the Himalayan region and North eastern states of India (excluding Assam) have relatively low densities while the Union Territories (excluding Andaman and Nicobar islands) have very high densities of population. |
Physical factor responsible for low density of population in Arunachal Pradesh is ______.
Hilly State
Lack of industries
Lack of transport network
Tribal population
Chapter:
Read the given source and answer the questions that follow:
|
Density of Population Density of population, is expressed as number of persons per unit area. It helps in getting a better understanding of the spatial distribution of population in relation to land. The density of population in India (2011) is 382 persons per sq. km. There has been a steady increase of more than 200 persons per sq. km over the last 50 years as the density of population increased from 117 persons/sq. km in 1951 to 382 persons/sq. km in 2011. Population densities in the country which ranges from as low as 17 persons per sq. km in Arunachal Pradesh to 11,297 persons in the National Capital Territory of Delhi. Among the Northern Indian States, Bihar (1102), West Bengal (1029) and Uttar Pradesh (828) have higher densities, while Kerala (859) and Tamil Nadu (555) have higher densities among the peninsular Indian States. States like Assam, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Jharkhand, Odisha have moderate densities. The hill states of the Himalayan region and North eastern states of India (excluding Assam) have relatively low densities while the Union Territories (excluding Andaman and Nicobar islands) have very high densities of population. |
How much excess is the density of population of Bihar in respect of average density of population of India?
720
417
741
471
Chapter:
Read the given source and answer the questions that follow:
|
Density of Population Density of population, is expressed as number of persons per unit area. It helps in getting a better understanding of the spatial distribution of population in relation to land. The density of population in India (2011) is 382 persons per sq. km. There has been a steady increase of more than 200 persons per sq. km over the last 50 years as the density of population increased from 117 persons/sq. km in 1951 to 382 persons/sq. km in 2011. Population densities in the country which ranges from as low as 17 persons per sq. km in Arunachal Pradesh to 11,297 persons in the National Capital Territory of Delhi. Among the Northern Indian States, Bihar (1102), West Bengal (1029) and Uttar Pradesh (828) have higher densities, while Kerala (859) and Tamil Nadu (555) have higher densities among the peninsular Indian States. States like Assam, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Jharkhand, Odisha have moderate densities. The hill states of the Himalayan region and North eastern states of India (excluding Assam) have relatively low densities while the Union Territories (excluding Andaman and Nicobar islands) have very high densities of population. |
Which of the following Union Territories has the highest density of population?
Andaman & Nicobar
Chandigarh
Lakshadweep
Puducherry
Chapter:
Read the given source and answer the questions that follow:
|
Density of Population Density of population, is expressed as number of persons per unit area. It helps in getting a better understanding of the spatial distribution of population in relation to land. The density of population in India (2011) is 382 persons per sq. km. There has been a steady increase of more than 200 persons per sq. km over the last 50 years as the density of population increased from 117 persons/sq. km in 1951 to 382 persons/sq. km in 2011. Population densities in the country which ranges from as low as 17 persons per sq. km in Arunachal Pradesh to 11,297 persons in the National Capital Territory of Delhi. Among the Northern Indian States, Bihar (1102), West Bengal (1029) and Uttar Pradesh (828) have higher densities, while Kerala (859) and Tamil Nadu (555) have higher densities among the peninsular Indian States. States like Assam, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Jharkhand, Odisha have moderate densities. The hill states of the Himalayan region and North eastern states of India (excluding Assam) have relatively low densities while the Union Territories (excluding Andaman and Nicobar islands) have very high densities of population. |
Which of the following north-eastern States has the lowest density of population?
Nagaland
Arunachal Pradesh
Sikkim
Meghalaya
Chapter:
Study the given graph carefully and answer the following question:
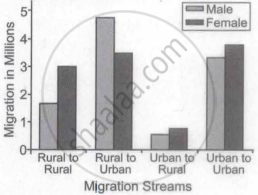
(Inter-state Migration by Place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams Period 0-9 years India, 2011)
Which one of the following streams has the highest 'male migration'?
Rural to Rural
Rural to Urban
Urban to Rural
Urban to Urban
Chapter:
Study the given graph carefully and answer the following question:

(Inter-state Migration by Place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams Period 0-9 years India, 2011)
In which of the following streams has the highest migration of females?
Rural to Urban
Urban to Rural
Rural to Rural
Urban to Urban
Chapter:
Study the given graph carefully and answer the following question:

(Inter-state Migration by Place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams Period 0-9 years India, 2011)
Which stream shows the least migration?
Rural to Rural
Rural to Urban
Urban to Rural
Urban to Urban
Chapter:

(Inter-state Migration by Place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams Period 0-9 years India, 2011)
What is the main reason of female migration in India?
Marriage
Employment
Education
Health
Chapter:
Study the given table and answer the question that follow:
| Doubling Time of World Population | ||
| Period | Population | Time in which Population Doubles |
| 10,000 B.C. | 5 million | |
| 1650 A.D. | 500 million | 1500 years |
| 1804 A.D. | 1,000 million | 154 years |
| 1927 A.D. | 2,000 million | 123 years |
| 1974 A.D. | 4,000 million | 47 years |
| 2025 A.D. | 8,000 million projected figure |
51 years |
It took 1500 years for population to reach 5 million to 500 million. If it is considered as the 'first stage of demographic transition', which of the following is the main reason for the slow pace of population growth?
High birth rate, Low death rate
High birth rate, High death rate
Low birth rate, High death rate
Low birth rate, Low death rate
Chapter:
Study the given table and answer the question that follow:
| Doubling Time of World Population | ||
| Period | Population | Time in which Population Doubles |
| 10,000 B.C. | 5 million | |
| 1650 A.D. | 500 million | 1500 years |
| 1804 A.D. | 1,000 million | 154 years |
| 1927 A.D. | 2,000 million | 123 years |
| 1974 A.D. | 4,000 million | 47 years |
| 2025 A.D. | 8,000 million projected figure |
51 years |
In which period did the population increase rapidly?
1927 - 1974
10,000 B.C. - 1650 A.D.
1804 - 1927
1650 - 1804
Chapter:
Study the given table and answer the question that follow:
| Doubling Time of World Population | ||
| Period | Population | Time in which Population Doubles |
| 10,000 B.C. | 5 million | |
| 1650 A.D. | 500 million | 1500 years |
| 1804 A.D. | 1,000 million | 154 years |
| 1927 A.D. | 2,000 million | 123 years |
| 1974 A.D. | 4,000 million | 47 years |
| 2025 A.D. | 8,000 million projected figure |
51 years |
How long did it take for the population to reach 1000 million to 4000 million?
123 years
170 years
277 years
221 years
Chapter:
Study the given table and answer the question that follow:
| Doubling Time of World Population | ||
| Period | Population | Time in which Population Doubles |
| 10,000 B.C. | 5 million | |
| 1650 A.D. | 500 million | 1500 years |
| 1804 A.D. | 1,000 million | 154 years |
| 1927 A.D. | 2,000 million | 123 years |
| 1974 A.D. | 4,000 million | 47 years |
| 2025 A.D. | 8,000 million projected figure |
51 years |
Population explosion is the result of which of the following stages?
First
Second
Third
Fourth
Chapter:
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Geography with solutions 2021 - 2022
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Geography-2022 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Geography, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Geography will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
